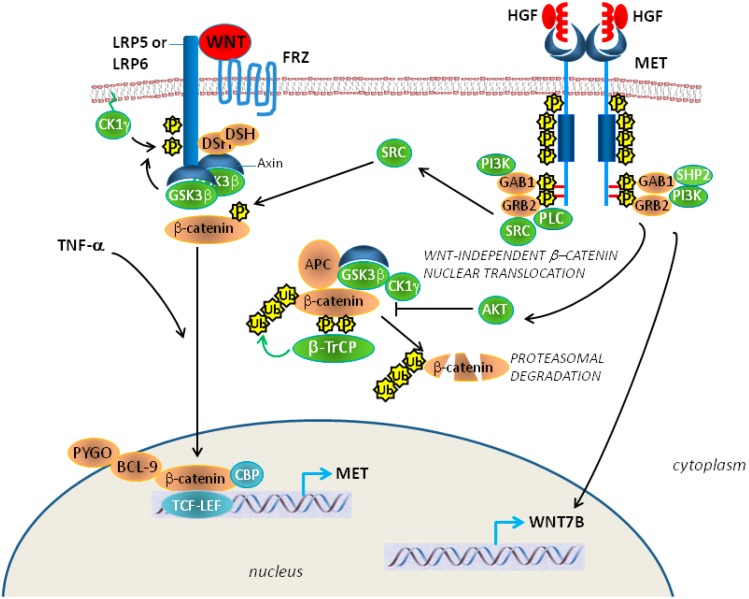
Figure 4.
Met and Wnt-β-catenin signaling pathways cooperate in regulating EMT (epithelial-mesenchymal transition). MET contributes to transcriptional activation of Wnt ligands, such as WNT7B. Met contributes to nuclear translocation of β-catenin by its tyrosine phosphorylation (directly or indirectly by SRC), or by inhibition of the β‑catenin degradation complex by Akt that phosphorylates glycogen synthase kinase‑3β (GSK3β). β‑TrCP, β‑transducin repeat-containing protein; APC, adenomatous polyposis coli; CBP, CREB-binding protein; CK1, casein kinase 1; DSH, disheveled; FRZ, frizzled; GAB1, GRB2‑associated-binding protein 1; GRB2, growth factor receptor-bound protein 2; LRP, low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein; PLC, phospholipase C; TCF-LEF, β-catenin target genes; TNF-α, Tumor Necrosis Factor-α; PYGO, pygopus. Modified from [80] with permission of NPG.