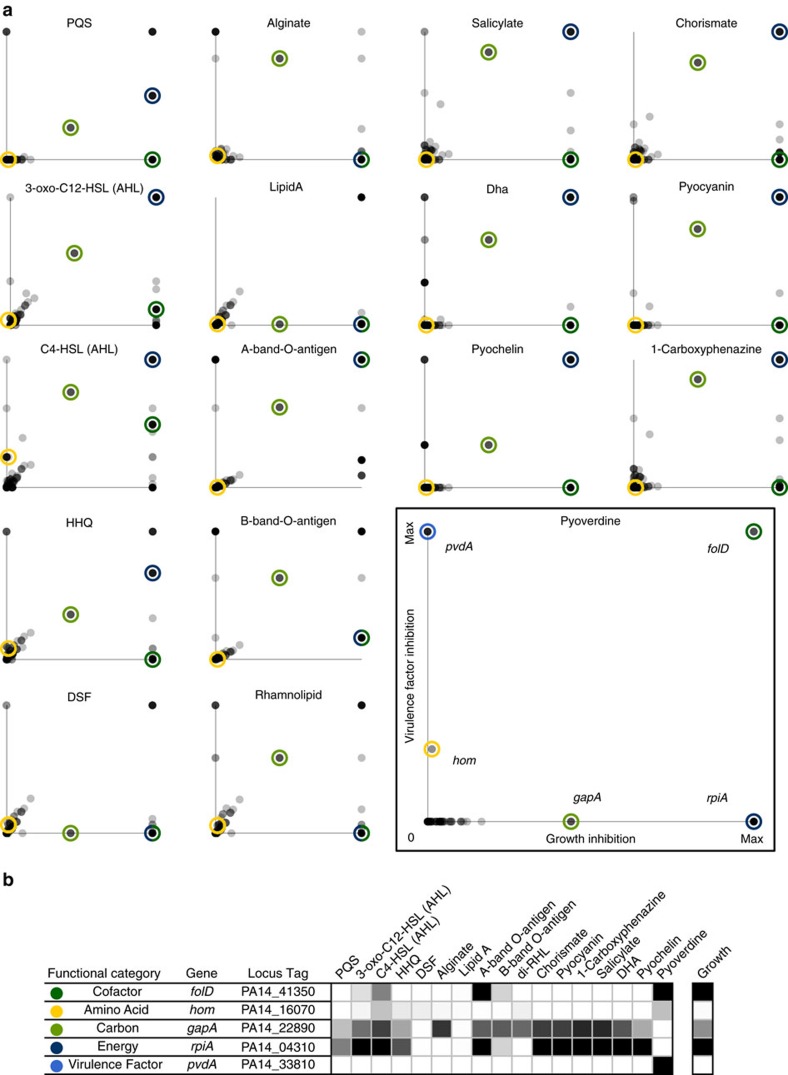
Figure 4. VF synthesis and growth interconnectivity.
(a) In silico gene knockouts were performed and the subsequent levels of biomass and VF production for each VF in the model were measured. The amount of growth inhibition was calculated by normalizing the knockout biomass production to the wild-type biomass production. Likewise, the amount of VF synthesis inhibition was calculated by normalizing the mutant level of VF production to the wild-type level of VF production. Each point indicates the growth inhibition (x axis) and VF inhibition (y axis) relative to wild-type for a given in silico knockout. All data points are transparent such that a high density of data points results in an increase in colour intensity. Coloured circles are used to indicate genes of interest as labelled in the pyoverdine example with yellow representing genes involved in amino acid metabolism, green carbohydrate metabolism, dark blue energy metabolism and light blue VF metabolism. (b) We highlight genes representing unique subtypes of impact on pyoverdine synthesis versus growth in a quantitative way that enables easy comparison of the activity of these genes across all VFs, with white indicating 0% inhibition and black indicating 100% inhibition.