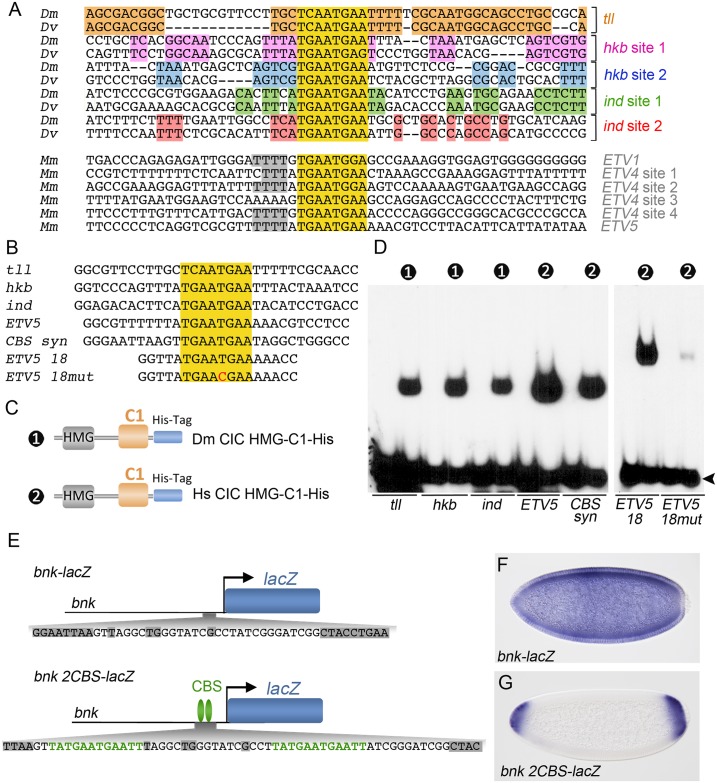
Fig 6. CIC recognizes individual octameric sites and does not depend on helper sites for selecting its targets.
(A) Alignment of sequences flanking functional CBSs from selected D. melanogaster (Dm), D. virilis (Dv) and mouse (Mm) CIC target genes. The CBSs are highlighted in yellow. Conserved flanking motifs are shaded in different colors. (B) Sequences of probes containing intact or mutated CBSs. (C) Diagram of recombinant Drosophila (Dm) and human (Hs) CIC constructs used in the EMSA experiments; both constructs were produced in bacteria. (D) EMSA analyses using the DNA probes and proteins shown in panels B and C, respectively. Numbers indicate the constructs used in the binding reactions; unlabeled lanes are negative controls without added protein. Free probes are indicated by an arrowhead. (E) Diagram of a control bnk-lacZ reporter and a modified version carrying two CBSs (bnk 2CBS-lacZ). The positions of the inserted CBSs are indicated below the reporters, with conserved motifs among Drosophila species shaded in grey. (F, G) Patterns of expression of bnk-lacZ and bnk 2CBS-lacZ reporters.