Fig 8. Distinct modes of target recognition by sequence-specific HMG-box proteins.
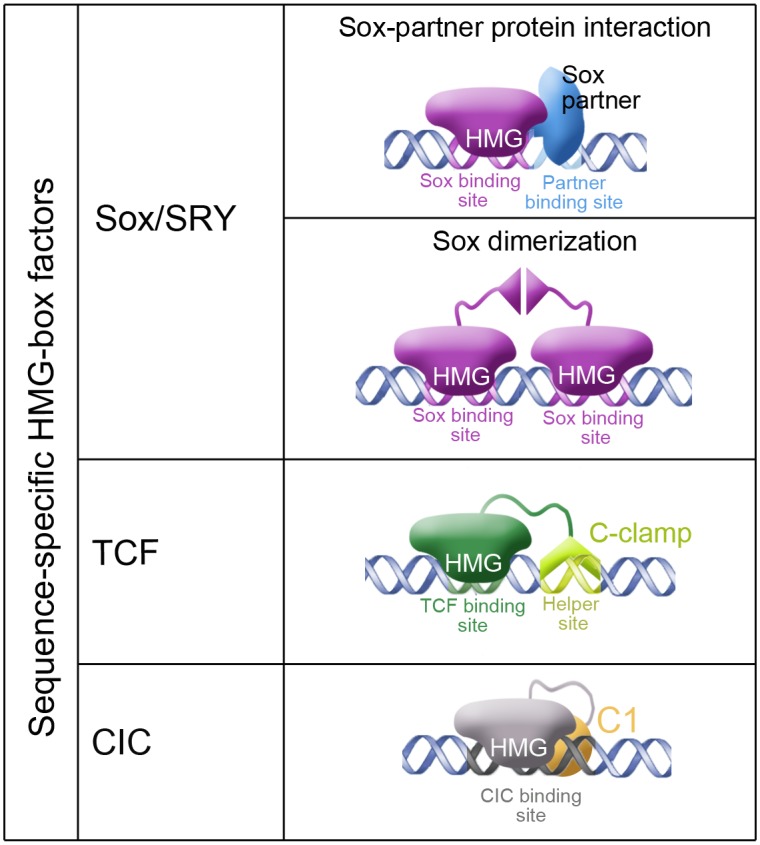
The diagram summarizes the main DNA-binding mechanisms used by each HMG-box sub-family. Sox proteins usually bind their Sox sites in combination with partner factors that recognize adjacent DNA sequences, but can also form homo- and heterodimers via specific dimerization motifs such as those present in SoxD and SoxE family members. Some TCF factors also exhibit bi-partite DNA recognition via the HMG-box and the C-clamp domain that binds GC-rich sequences known as Helper sites. In contrast, CIC proteins appear to bind individual octameric sites through their HMG-box and C1 domains, acting independently of other specific DNA sites and partner proteins.
