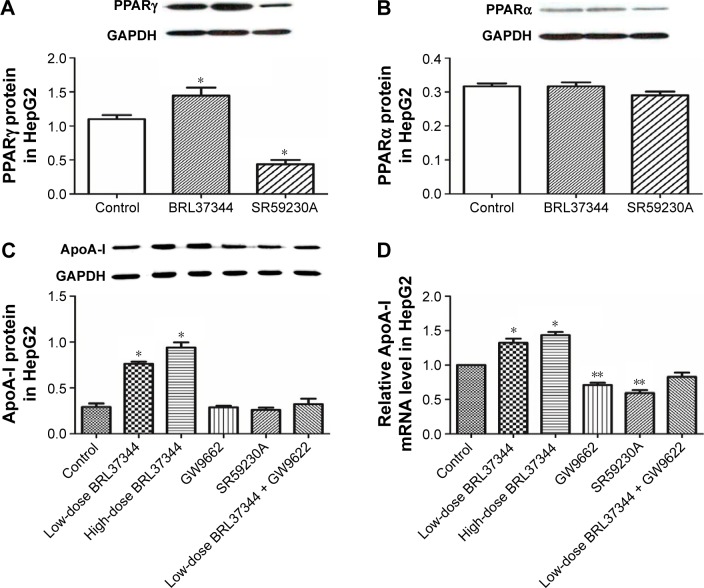
Figure 4.
Elevated ApoA-I expression by β3-adrenoceptor activation is abolished by PPARγ antagonist in HepG2 cells.
Notes: (A and B) Western blot analysis of PPARγ and PPARα in HepG2 cells after BRL37344 treatment. Control: HepG2 cells with DMSO treatment; BRL37344: HepG2 cells with 24 h 10−6 mol/LBRL37344 treatment; SR59230A: HepG2 cells with 10−6 mol/L SR59230A treatment. (C and D) Western blot analysis and RT-PCR analysis of ApoA-I protein and mRNA expressions, respectively, in HepG2 cells after BRL37344 treatment with or without PPAR antagonist GW9662. Control group: HepG2 cells with DMSO treatment; low-dose BRL37344 group: HepG2 cells treated with 10−6 mol/L BRL37344; high-dose BRL37344 group: HepG2 cells treated with 10−5 mol/L BRL37344; GW9662 group: HepG2 cells treated with 10 μmol/L GW9662 only; SR59230A group: HepG2 cells treated with 10−6 mol/L SR59230A; and low-dose BRL37344 + GW9662 group: HepG2 cells with 10−6 mol/L BRL37344 and 10 μmol/L GW9662 treatment. Statistically significant differences are indicated (compared with control group, *P<0.01; **P<0.05).
Abbreviations: Apo, apolipoprotein; GAPDH, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; PPAR, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor; RT-PCR, real-time PCR.