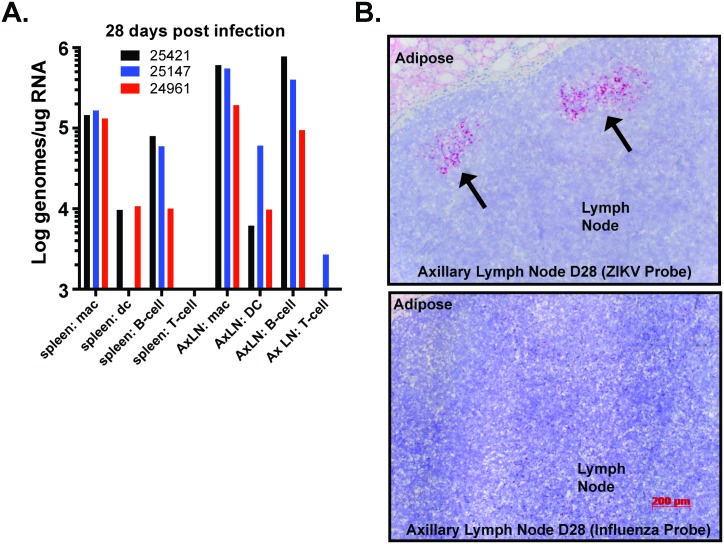
Fig 4. Infected cell types in spleen and axillary lymph nodes of ZIKV-infected rhesus macaques.
Cell subpopulations were isolated by positive selection magnetic bead separation from lymphocytes isolated from the spleen and axillary lymph nodes at 28 dpi. For macrophage and T cell isolation, CD14-microbeads were used to isolate macrophages from total spleen and axillary lymph node lymphocytes, and then anti-CD3 was used to isolate T cells from macrophage depleted flow-through. For B cell and DC isolation, total splenocytes or axillary lymph node lymphocytes were first positively selected for CD20+ B cells and the depleted fraction was bound to CD1c microbeads to isolate DCs. To increase purity of the isolated cell populations all positively selected samples were eluted after primary selection and then re-bound to a second fresh column. Depiction of isolated cell populations as characterized by flow cytometry is shown in S4 Fig. Total RNA was isolated from the positively selected cell fractions and quantified. One-step qRT-PCR was used to measure ZIKV RNA loads in each of the cell fractions isolated from animals at 28dpi (A). Viral RNA loads were highest in the macrophage and B cell fractions, with consistently less vRNA detected in DCs and rarely in the T cells. (B) Serial paraffin sections of axillary lymph node tissue from animal #25421 were hybridized with ZIKV specific chromogenic probe (red) or Influenza specific chromogenic probe (red) and counterstained with hematoxylin (blue) showed strong positive staining for ZIKV in the lymphoid follicles. Original magnification was 50X.