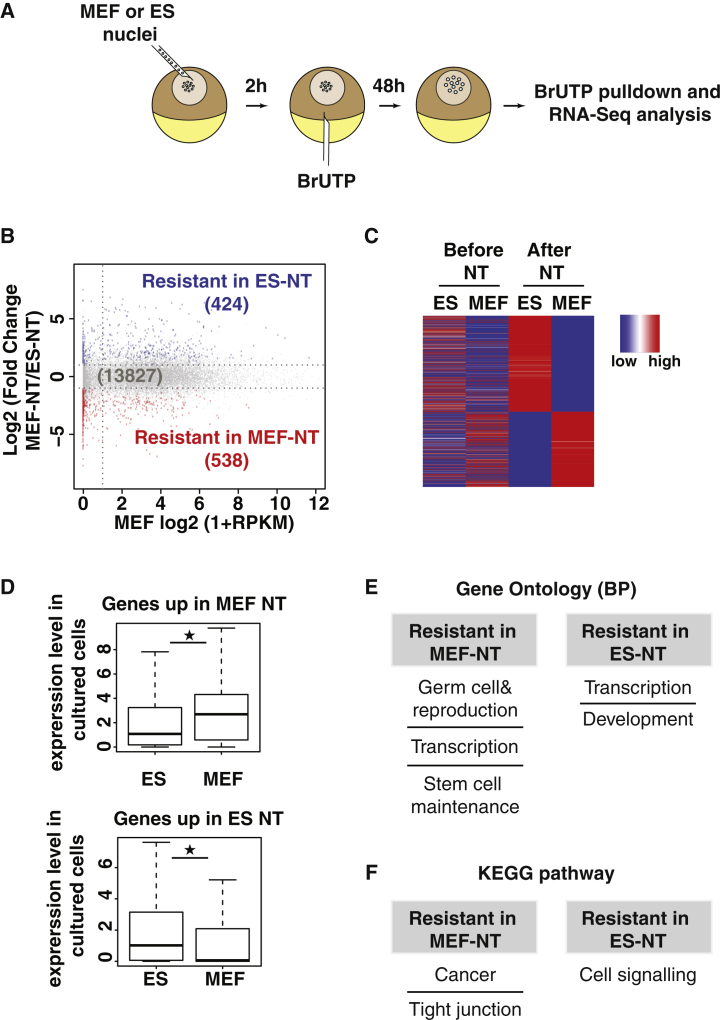
Figure 1.
Identification of Genes Resisting Transcriptional Reprogramming by Oocytes
(A) Schematic representation shows the nuclear transplantation strategy used to identify genes resistant to reactivation by Xenopus oocytes.
(B) MA plot shows log fold change (logFC, y axis) in gene expression between MEF-NT versus ES-NT against the expression in cultured MEFs (x axis, log2 reads per kilobase per million mapped reads [RPKM]; data from Reddington et al., 2013). Red and blue dots, genes differentially expressed (FDR < 0.05, two experiments, n = 32 NT samples per condition).
(C) Heatmap representing expression of the differentially expressed genes (rows, Z score of normalized expression level) between MEF-NT and ES-NT in ES and MEF before and 48 hr after NT (columns, genes sorted according to fold change between MEF-NT to ES-NT). Expression data for cells before NT are from Reddington et al. (2013) and Bulut-Karslioglu et al. (2014).
(D) Boxplot shows the gene expression level before and after NT of genes resistant in MEF-NT (538 genes, top) or resistant in ES-NT (424 genes, bottom). ★p value < 10−6, Wicoxon rank-sum test.
(E and F) The top (E) gene ontology terms and (F) KEGG pathways enriched in the list of differentially expressed (DE) genes restricted in MEF-NT and ES-NT. See also Figure S1 and Tables S1 and S2.