Figure 4.
Multiple Chromatin Modifier Combinations Affect Resistance at a Single-Gene Level
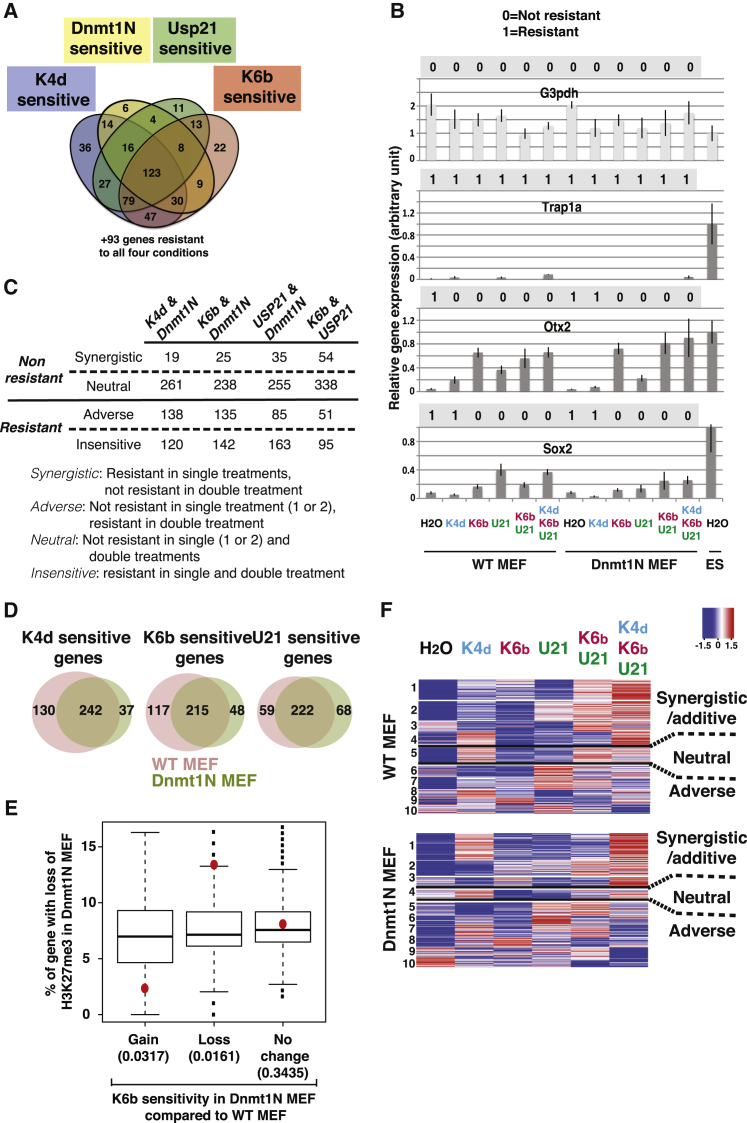
(A) Venn diagram shows the number of genes losing resistance upon four individual chromatin modifier treatments.
(B) Example of digital signature of resistance obtained by differential gene expression analysis for a non-resistant (G3pdh) and three resistant (Trap1A, Otx2, and Sox2) genes. The digital signature indicates whether a gene is resistant (shown as 1 when the gene is differentially expressed in MEF-NT compared to ES-NT) or loses resistance (shown as 0, when the gene is not differentially expressed in MEF-NT compared to ES-NT) in each of the 12 conditions tested. The bar graphs show qRT-PCR analysis of gene expression (mean ± SEM of four samples of eight oocytes NT).
(C) The numbers of genes for which a synergistic, neutral, adverse, or insensitive effect is observed when combining two chromatin modifier treatments are shown.
(D) Venn diagram shows the number of genes sensitive to a histone modifier (Kdm4d, Kdm6b, or USP21) in nuclei with normal (WT) or hypomethylated DNA (Dnmt1N).
(E) Loss of resistant gene sensitivity to Kdm6b in DNA-hypomethylated MEF correlates with loss of H3K27me3. The y axis indicates the number of genes that lose H3K27me3 in MEF with hypomethylated DNA compared to WT MEF. Resistant genes are split according to change in sensitivity to Kdm6b after NT when comparing WT MEF to MEF with hypomethylated DNA (red dot). The boxplot shows the background distribution of H3K27me3 change when sampling 10,000 times for a random set of genes of the same size as the resistant gene subset tested. The number in parentheses indicates a p value generated by calculating the proportion of the random background that has a more extreme value than the observed percentages from each of the three groups.
(F) Heatmap illustrating the change in gene expression in normal (WT MEF nuclei) or hypomethylated DNA (Dnmt1N MEF nuclei) upon expression of histone modifiers. Ten clusters representing the main trend of gene expression change were selected based on k-means clustering of expression data from RNA-seq analysis (RPKM). The trend of change in gene expression in these ten clusters is shown in the heatmap as a Z score. See also Table S4.