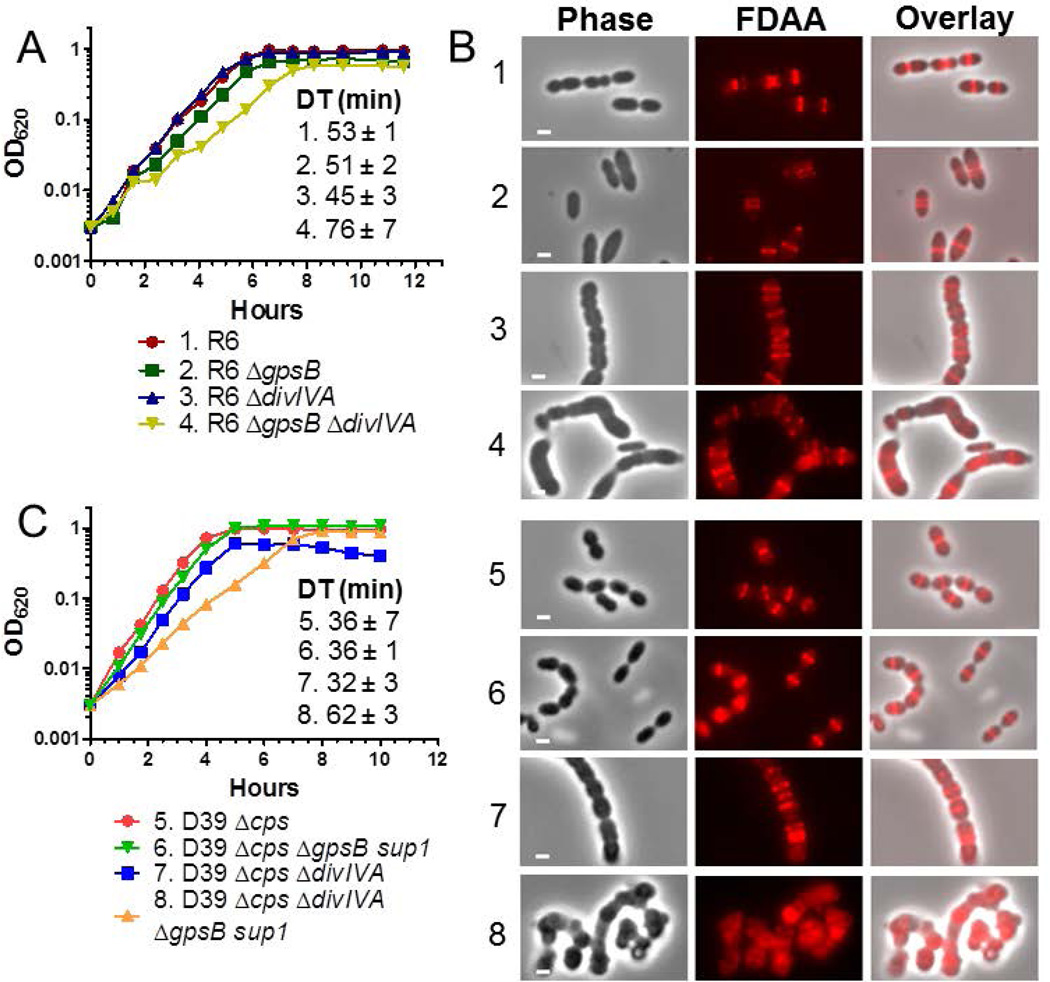
Fig. 1.
ΔdivIVA mutations are not epistatic to ΔgpsB in pneumococcal strains R6 and D39. A) Representative growth curves of R6 strains. Isogenic strains listed as 1–4 are: 1, R6 (EL59); 2, R6 ΔgpsB (IU8224); 3, R6 ΔdivIVA (IU8371); 4, R6 ΔgpsB ΔdivIVA (IU8369). Average doubling times (±SEM) from 2 independent experiments were calculated for OD620 ≈ 0.015 to 0.2 using a nonlinear regression exponential growth curve program (GraphPad Prism). B) Fluorescent D-amino acid (FDAA) staining and microscopy of live cells labeled with FDAA for 5 min were performed as described in Experimental procedures. The panels shown from left to right are: phase, FDAA, and a phase/FDAA overlay. Genotypes are indicated according to the numbers in panels A and C. Representative images are shown of ≥95% of the cells (n>50 for R6 strains; n>70 for D39 strains) examined manually of each strain. C) Representative growth curves of D39 Δcps strains and D39 Δcps ΔgpsB sup1 strains, which contain a suppressor mutation (phpP(G229D)) of ΔgpsB as described in the text. Isogenic strains listed as 5–8 are: 5, D39 Δcps (IU1945); 6, D39 Δcps ΔgpsB phpP(G229D) (IU6442); 7, D39 Δcps ΔdivIVA (IU8496); 8, D39 Δcps ΔgpsB phpP(G229D) ΔdivIVA (IU11205). Doubling times were calculated as described above. Independent experiments were performed two to three times with similar results. Scale bar = 1 micron.