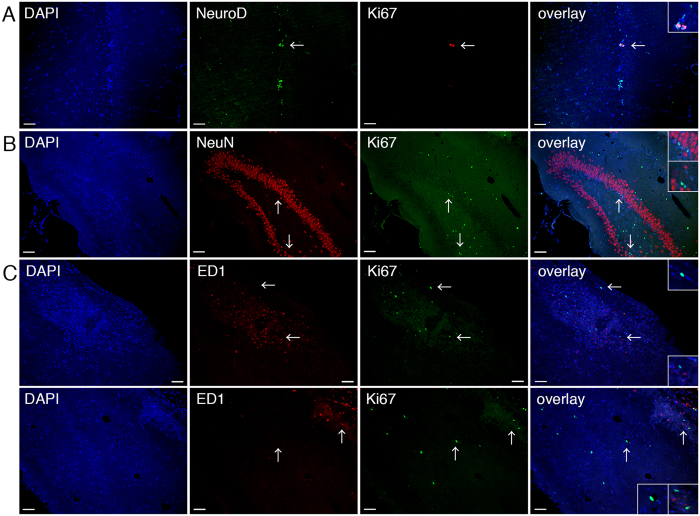
Figure 6. The majority of Ki67-positive cells in the ipsilateral hippocampus were NeuN- and ED1-negative.
(A) Representative photomicrographs of the double staining of Ki67 and NeuroD in the ipsilateral hippocampus of an SCE-UCBC-treated rat. DAPI (blue), anti-NeuroD antibody (green), and anti-Ki67 antibody (red) staining, rightmost panel, overlay. A small portion of Ki67-positive cells was NeuroD-positive (7 cells out of 132 Ki67-positive cells in the ipsilateral hippocampus, 5.3%, n = 8; 3 cells out of 35 Ki67-positive cells in the ipsilateral SGZ, 8.6%, n = 8). The double-positive NeuroD/Ki67 cells are shown in A. (B) Representative photomicrographs of the double staining of Ki67 and NeuN in the ipsilateral hippocampus of an SCE-UCBC-treated rat. DAPI (blue), anti-NeuN antibody (red), and anti-Ki67 antibody (green) staining, rightmost panel, overlay. The Ki67-positive cells were NeuN-negative (0 cells out of 114 Ki67-positive cells, n = 3). (C) Representative photomicrographs of the double staining of Ki67 and ED1 in the ipsilateral hippocampus of a control rat (upper panels) and SCE-UCBC-treated rat (lower panels). DAPI (blue), anti-ED1 antibody (red), and anti-Ki67 antibody (green) staining, rightmost panel, overlay. The Ki67-positive cells were ED1-negative (0 cells out of 99 Ki67-positive cells in the ipsilateral hippocampus of an SCE-UCBC-treated rat, n = 3). The specimens containing the greatest number of Ki67-positive cells were selectively shown in this figure, making it easier to recognize the type of proliferating cells. Insets show higher magnification views. Arrows indicate the area magnified. Bar, 50 μm.