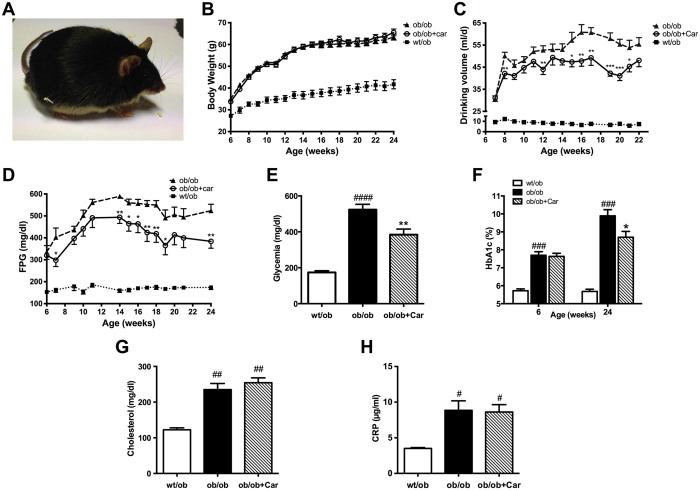
Figure 1. Carnosine attenuates diabetes in BTBR ob/ob mice.
(A) Representative image of a 24-week-old BTBR ob/ob mouse. (B) Body weight increased in ob/ob mice, independent of carnosine treatment. (C) Daily water intake was increased in ob/ob mice relative to wt/ob mice, and attenuated in carnosine-administered animals. (D) Weekly determination of fasting plasma glucose (FPG) indicated manifest hyperglycemia in ob/ob mice, which was reduced in carnosine-treated animals throughout the observation period. (E) Random glycemia (measured before perfusion) was significantly lower in carnosine-administered ob/ob mice compared with ob/ob controls. (F) At week 24 of age (18 weeks of treatment), HbA1c levels of ob/ob animals were elevated, and significantly reduced in carnosine treated mice. (G and H) Serum cholesterol and C-reactive protein (CRP) (at week 24 of age) were elevated in ob/ob mice, and unaffected by carnosine. Data represents means ± SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 compared to ob/ob mice. #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01, ###P < 0.001, ####P < 0.0001 compared to wt/ob mice. Car: carnosine.