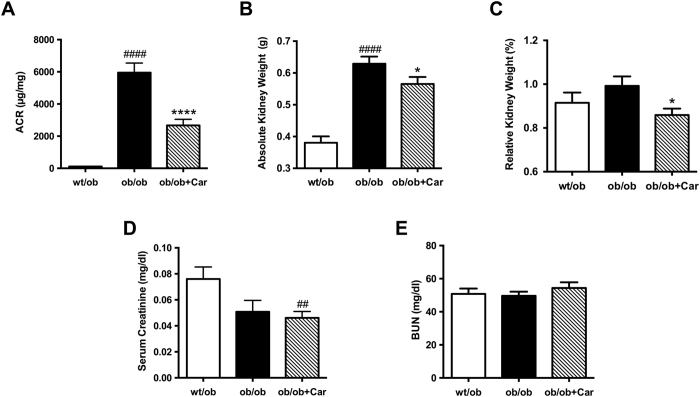
Figure 3. Carnosine protects from diabetic kidney damage.
(A) Carnosine administration for 18 weeks significantly reduced the ACR at week 24 by more than twofold compared with the ob/ob controls. (B) At the end of the experiment, kidney weight (average of both kidneys) was significantly increased in ob/ob mice, which was attenuated in carnosine-treated mice. (B and C) At the end of the experiment, the absolute kidney weight (average of both kidneys) was significantly increased in ob/ob mice. Carnosine treatment resulted in both reduced absolute and relative kidney weights. (D and E) Serum creatinine and blood urea nitrogen (BUN) were determined at the end of the experiment. The highest serum creatinine levels were found in heterozygous mice, being significantly different from the lowest levels found in carnosine-supplemented homozygous mice. No differences were observed with respect to BUN between any of the groups. Data represents means ± SEM. *P < 0.05, ****P < 0.0001 compared to ob/ob mice. ##P < 0.01, ####P < 0.0001 compared to wt/ob mice. Car: carnosine.