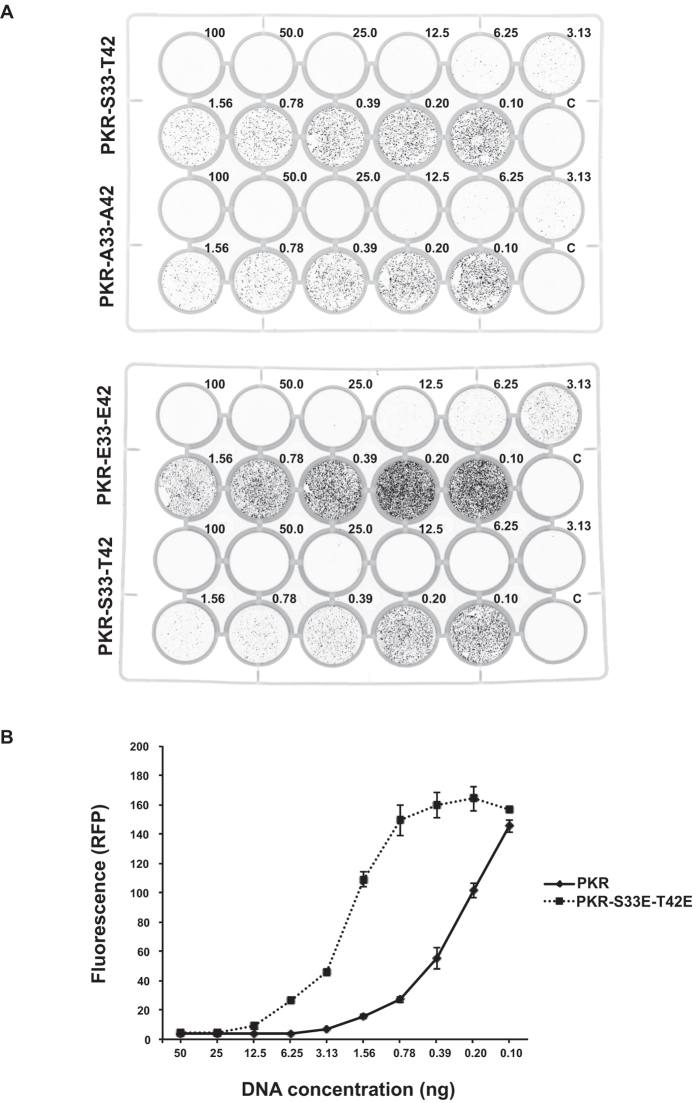
Figure 7. S33 and T42 phosphor-residues control PKR activity.
(A) Representative images of cell culture plates demonstrating RFP expression in HEK293 cells transfected with an RFP-reporter of protein translation (20 ng/well) and the designated amounts of the indicated PKR constructs (ng/well). The relative effect of mutating S33 and T42 to alanine (A33-A42) is compared to the wild type (S33-T42) in the upper plate and the glutamic acid phosphor-residue mutant (E33-E42) is compared to wild-type PKR in the lower plate. (B) A quantitation of the activity of the wild-type (S33-T42) and glutamic acid phosphor-residue mutant (E33-E42) PKR constructs transfected into HEK293 cells, as assessed by their relative control of the RFP reporter of protein translation. The graph shows the total fluorescence per well produced in replicated experiments as shown in (A). The data are produced with PKR constructs generated for the bimolecular complementation assays and are expressed with an N-terminal V1 tag. The response of constructs alternatively tagged with the V2 split Venus are shown as Supplementary Figure S5. Error bars show the SEM. Student’s t test was used to calculate the p values. For all data points, except those for plasmid DNA concentrations of 50, 25, 0.2 and 0.1 ng/well, p values were <0.001 (n = 4).