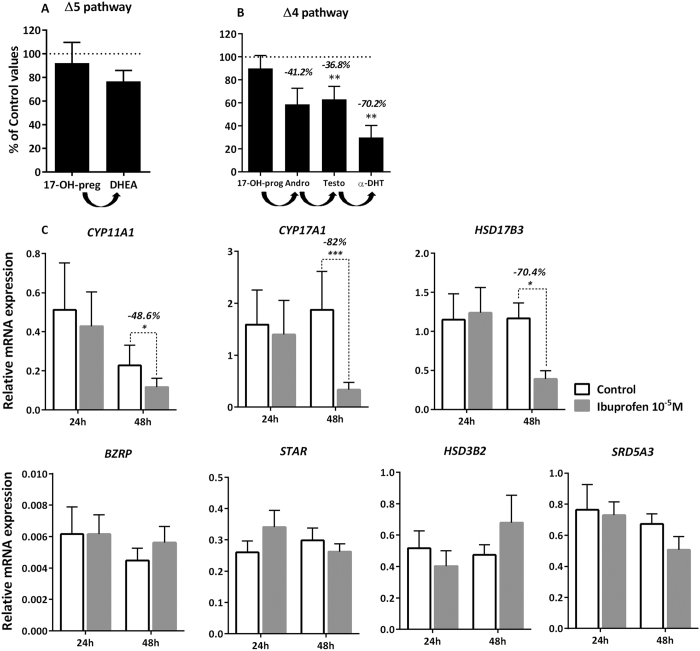
Figure 2. Ibuprofen and global steroidogenesis.
(A,B) Global analysis of ibuprofen effects on the Δ5 (A) and Δ4 pathways (B) of testosterone production using GC-MS/MS. Human fetal testis explants (8–9.9 GW) were incubated for 48 h with DMSO (Control) or 10−5 M of ibuprofen. Steroid precursors of the Δ5 and Δ4 pathways were measured by GC-MS/MS in the media. Values are mean ± SEM of 8 fetuses pooled in 5 independent experiments, and are expressed as the percentage of variation from the control. **p < 0.01 by non-parametric signed rank Wilcoxon test on paired data. (C) Quantitative RT-PCR of BZRP, STAR, CYP11A1, CYP17A1, HSD17B3, HSD3B2 and SRD5A3 was performed on control testes (white bars) and testes treated with 10−5 M of ibuprofen (grey bars) for 24 and 48 h. Each column shows a pool of 11–15 fetal testes. Each bar represents the mean ± SEM of the fold change in target gene expression relative to the reference gene RPLP0. A non-parametric signed rank Wilcoxon test on paired data was performed (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001).