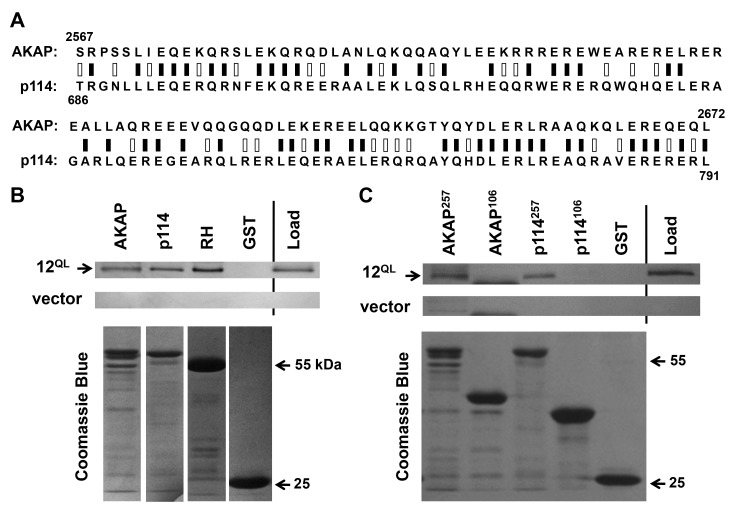
Figure 2.
A conserved Gα12-binding domain in AKAP-Lbc and p114RhoGEF. (A) Sequence alignment of AKAP-Lbc and p114RhoGEF. Results of Protein BLAST (blastp) analysis are displayed, with black bars indicating identical residues (50/106), white bars indicating non-identical positive matches (28 additional residues), and zero gaps. (B) Interaction of Gα12 with regions of p114RhoGEF and AKAP-Lbc. Co-precipitation experiments were performed as described in Methods, using GST-fusions of the 257-amino acid C-terminus of AKAP-Lbc (AKAP), the corresponding 257 residues of p114RhoGEF (p114), amino acids 2-252 of p115RhoGEF containing its RH domain (RH), and GST alone. Load samples were set aside prior to addition of Sepharose-bound GST-fusion proteins. Co-precipitations from HEK293 cells transfected with myc-tagged, constitutively activated Gα12 (12QL) and empty vector were performed in parallel. For each sample, 20% of precipitated material was examined by SDS-PAGE/Coomassie Blue staining to assess levels of GST-fusion proteins, shown in lower panels. (C) Co-precipitations using the closely homologous, 106-amino acid domains within the Gα12-binding, 257-residue regions of AKAP-Lbc (AKAP) and p114RhoGEF (p114) are shown. Amino acid lengths of these adducts to GST are indicated as superscripts. Results in (B) and (C) are representative of three or more independent experiments.