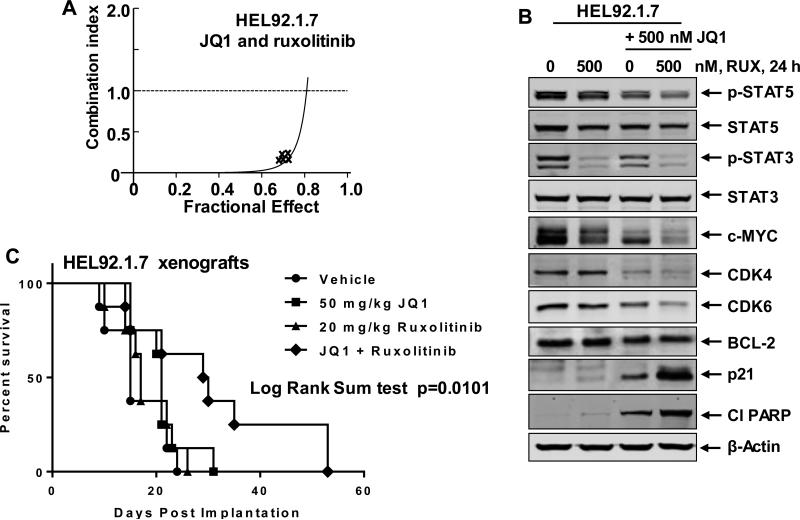
Figure 4. Co-treatment with JQ1 and JAK inhibitor ruxolitinib synergistically induces apoptosis of cultured sAML cells and improves the survival of mice bearing HEL92.1.7 cell xenografts.
A. HEL92.1.7 were treated with JQ1 (dose range: 200-1000 nM) and ruxolitinib (dose range: 200-1000 nM) at a constant ratio for 48 hours. Then, the % of annexin V- and TO-PRO-3-iodide positive, apoptotic cells was determined by flow cytometry. Median dose effect and isobologram analyses were performed utilizing CompuSyn, assuming mutual exclusivity. Combination index (CI) values less than 1.0 indicate a synergistic interaction of the two agents in the combination. B. HEL92.1.7 cells were treated with the indicated concentrations of JQ1 and/or ruxolitinib for 24 hours. Following this, the cells were harvested and total cell lysates were prepared. Immunoblot analyses were conducted as indicated. The expression levels of β-actin in the lysates served as the loading control. C. HEL92.1.7 cells were injected into the lateral tail vein of NSG mice (n=8) that had been pre-conditioned with 2.5 Gy of gamma irradiation. Seven days post cell implantation, mice were treated with 50 mg/kg of JQ1 (daily × 5 days, by IP injection) and/or 20 mg/kg ruxolitinib (daily × 5 days, P.O.) for 3 weeks. The survival of the mice is represented by a Kaplan Meier plot.