Figure 1.
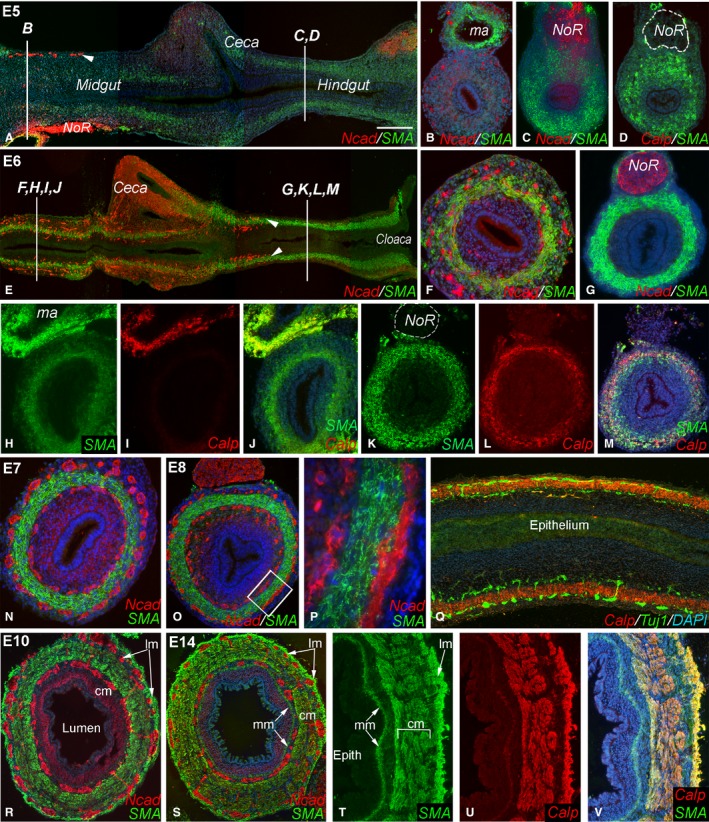
Coordinated development of smooth muscle and enteric nervous system (ENS) during chick gut development. At E5, smooth muscle actin (SMA) expression is very low in the mid‐gut and ceca (A,B). While SMA is present in the hindgut at E5, calponin is not (C,D). At E5, the enteric neural crest‐derived cell (ENCC) wavefront is proximal to the cecal region (A, arrowhead; B). By E6, ENCCs have reached the proximal hindgut (E, arrowheads) and SMA is expressed in both mid‐gut (F) and hindgut (G). E6 mid‐gut expresses SMA but not calponin (H–J), although calponin expression in vascular smooth muscle in a mesenteric artery is seen (I). E6 hindgut expresses both muscle proteins (K–M). Circular smooth muscle and both plexuses are present in E7 mid‐gut (N) and E8 hindgut (O, boxed area magnified in P). E8 longitudinal section shows Tuj1+ enteric neurons on either side of the calponin‐expressing circular muscle layer (Q). By E10, longitudinal muscle layer has formed in the hindgut (R). At E14, the muscularis mucosa is visible (S) and all muscle layers express SMA and calponin (T–V). DAPI staining (when present) is blue. Scale bar: 200 μm (A); 140 μm (B–D); 260 μm (E); 120 μm (F); 100 μm (G); 125 μm (H–Q); 120 μm (45 μ; T–V); 370 µm (P); 120 μm (R). Calp, calponin; cm, circular muscle; epith, epithelium; lm, longitudinal muscle; ma, mesenteric artery; mm, muscularis mucosae; Ncad, N‐cadherin; NoR, nerve of Remak.
