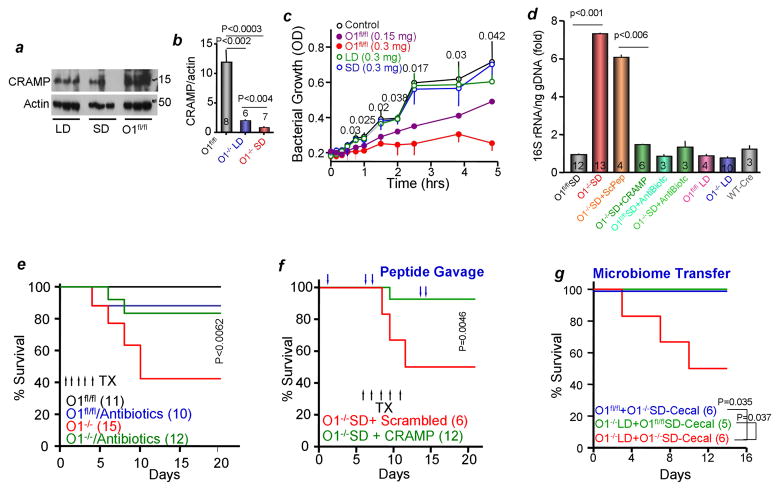
Figure 6. Pancreatic bacterial killing role in the gut microbiome.
(a, b) Pancreatic extracts from Orai1fl/fl and Orai1−/− mice maintained on liquid or solid diets were analyzed for total CRAMP. Shown are sample blots and the average from the indicated number of mice is given in the columns.
(c) Secreted antibacterial killing activity by Orai1fl/fl and Orai1−/− acinar cells stimulated with 100 pM CCK8 is tested as inhibition of E. coli growth. The results are mean±s.e.m of extracts obtained from 3 mice in each line.
(d) Cecal 16S rRNA extracted from the indicated number of mice that were treated with CRAMP or scrambled peptides or antibiotics and maintained on LD or SD was measured by qPCR. Results are expressed as mean±s.e.m.
(e) Survival of mice untreated or treated with wide-spectrum antibiotics for one week before and during the experiment provided in drinking water. TX, tamoxifen
(f) Survival of Orai1−/− SD mice after gavage at the time indicated by the blue arrows with 100 μg CRAMP peptide dissolved in 200 μl PBS. Control mice were gavaged with scrambled peptide.
(g) Microbiome transplant was accomplished by gavaging Orai1fl/fl (blue) and Orai1−/− mice maintained on liquid diet (red) with cecal bacteria from Orai1−/− mice maintained on solid diet. As an additional control, Orai1−/− mice maintained on liquid diet were gavaged with cecal bacteria from Orai1fl/fl mice (green).