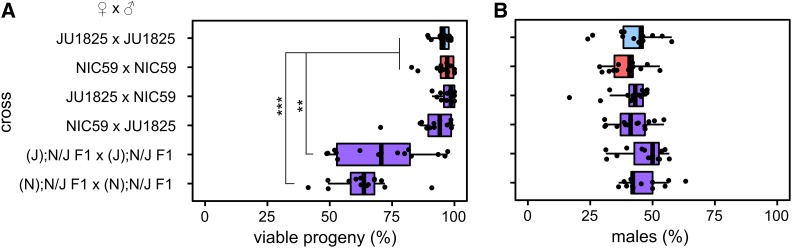
Figure 1.
JU1825 and NIC59 exhibit F2 hybrid breakdown. Crosses are listed on the y-axis. Letters in parentheses to the left of a semicolon denote the cytoplasmic genotype of an individual (for example, “(J)” individuals have a JU1825 cytoplasmic genotype), while letters to the right of a semicolon denote the genotypes of all autosomal loci (that is, “N/J” individuals are heterozygous NIC59/JU1825 throughout the autosomes). (A) Only (J); N/J F1 × (J); N/J F1 and (N); N/J F1 × (N); N/J F1 crosses exhibit a significant decrease in the percentage of viable progeny (P < 0.01 and P < 0.001, respectively). (B) There are no significant differences in the percentages of viable males between crosses (P > 0.05). N = 14 or 15 plates per cross. All P-values were calculated by a Kruskal–Wallis test followed by Dunn’s test.