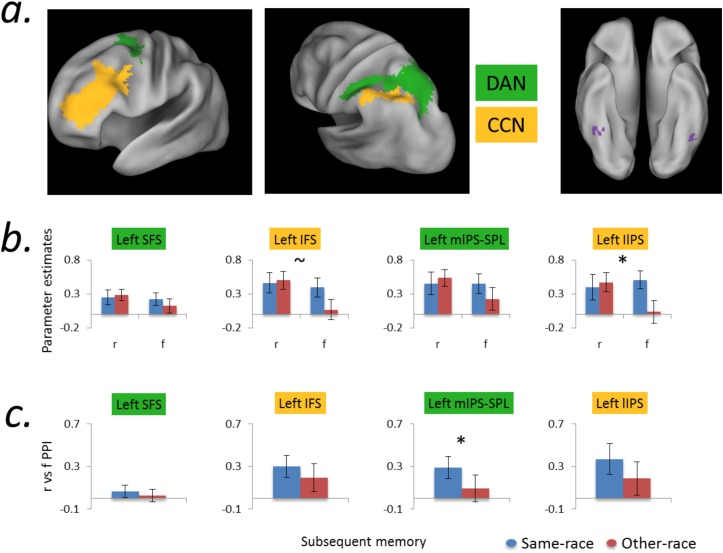
Fig 3. Subsequent Memory Effects as a function of the Other Race Effect.
a) Left panels: 3D renderings of dorsal attention network (DAN, green) and cognitive control network (CCN, orange) ROIs. Right panel: Group-level SME “parent” seeds (purple) for PPI analysis (Fig 3c). b) Univariate activity as a function of subsequent memory and same-/other-race face status. There was a tendency towards greater SMEs for other- than same-race faces in left frontoparietal components of the CCN; OREs on the SME were qualitatively similar, but quantitatively reduced, in frontoparietal components of the dorsal attention network. Specifically, the ORE on the SME reached significance in lateral IPS (CCN) and was at trend level in IFS (CCN). c) PPI SME analyses as a function of the ORE. Right fusiform SME connectivity during encoding was greater for same- than other-race faces in the bilateral parietal DAN nodes (right hemisphere not shown); qualitatively similar patterns were observed in the CCN. r = remembered; f = forgotten; SFS = superior frontal sulcus; IFS = inferior frontal sulcus; mIPS-SPL = medial IPS and superior parietal lobule; lIPS = lateral IPS. Error bars reflect group SEM. * = ORE × SME interaction significant at p<0.05, ~ = p<0.10.