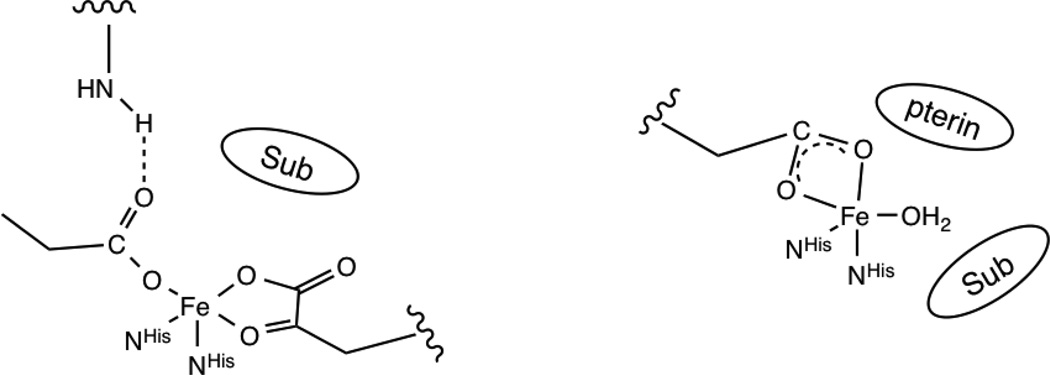
Figure 4.
Schematic comparison of facial triad coordination for the classes of NHFe enzymes that have a second-sphere residue hydrogen bonding to the coordinated carboxylate (αKG dependent enzymes, shown at left, and the extradiol dioxygenases), leading to monodentate coordination, and those without a hydrogen bonding residue (pterin dependent enzymes, shown at right, and the Rieske dioxygenases), which leads to bidentate carboxylate coordination.