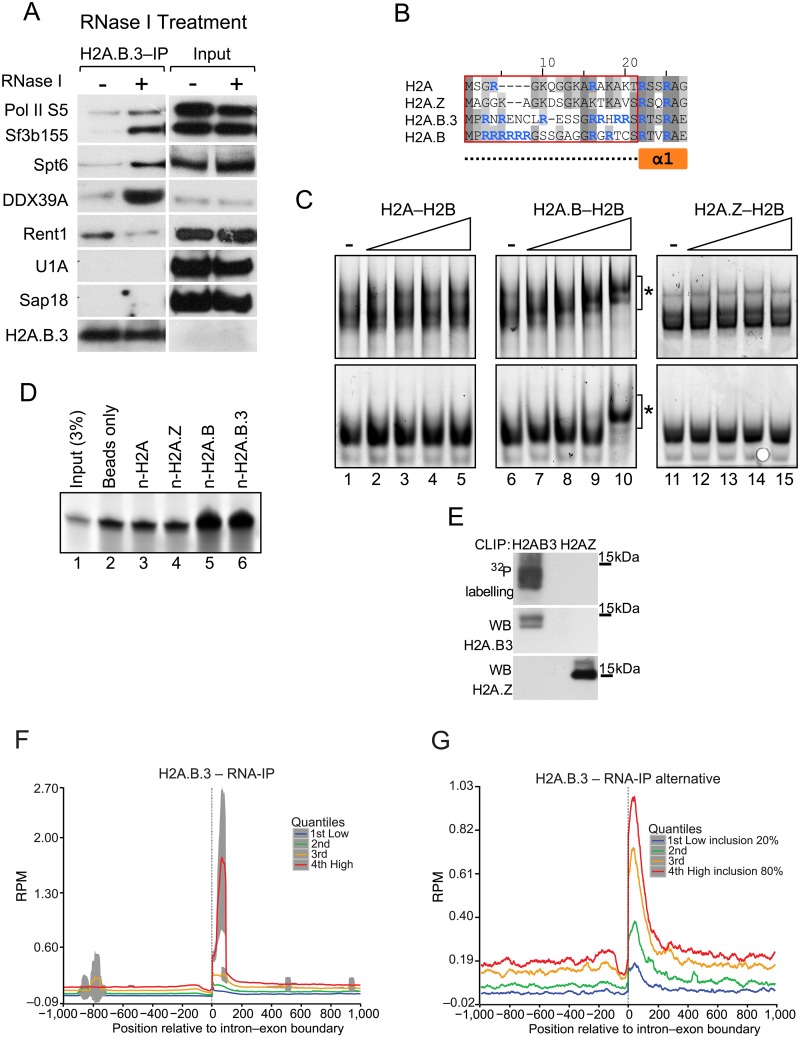
Fig 5. H2A.B.3 can bind RNA in vitro and in vivo.
(a) Total cellular lysates were prepared from UV treated mouse testes and treated with RNase I or not. H2A.B.3 was then immunoprecipitated and the co-immunoprecipitated proteins were identified by western blotting with the indicated antibodies selected to detect proteins involved in different aspects of RNA synthesis, processing, and export. (b) Amino acid sequence alignment of the N-terminal region of histone H2A and the variants H2A.Z, H2A.B.3, and H2A.B. Compared to H2A, the N-terminus of H2A.B.3 and H2A.B are 6.3% and 23.5% identical, respectively. The red box demarcates the sequences corresponding to the N-terminal peptides used for the pulldown experiments in panel d, and corresponds to the unstructured region (dashed line) preceding the first alpha helix of H2A (α1; orange box). Arginine residues are highlighted in blue. (c) Histone dimer samples (0.6, 1.1, 2.3, 4.5 μM) were incubated with 20 ng in vitro transcribed RNA (222 nt and 152 nt, top and bottom panels, respectively) and analysed on 5% acrylamide 1X TB gels. The asterisk (*) denotes shifted bands corresponding to H2A.B—H2B-RNA complexes. (d) An RNA pulldown assay using biotinylated histone N-terminal peptides (n-H2A, n-H2A.Z, n-H2A.B and n-H2A.B; 130 pmol). Samples were run on 15% TBE-Urea gels, along with input RNA (5 pmol; 3% of total input) for comparison. (e) CLIP assays demonstrating that H2A.B.3 but not H2A.Z directly interacts with RNA in germ cells. Also show is the western blot analysis of the immunoprecipitated H2A.B.3 and H2A.Z. Following the RNA—IP procedure (see Methods), cells isolated from 28–30 day old testes were UV crosslinked, the chromatin sheared and following the immunopurification of H2A.B.3-containing chromatin fragments, the released RNA was sequenced to yield 100 base pair paired end reads. (f) H2A.B.3 RNA plot ranked according to expression aligned with all intron—exon boundaries. (g) A H2A.B.3 RNA plot ranked according to the level of exon inclusion (20 to 80%) aligned with the intron—exon boundary of alternatively spliced exons.