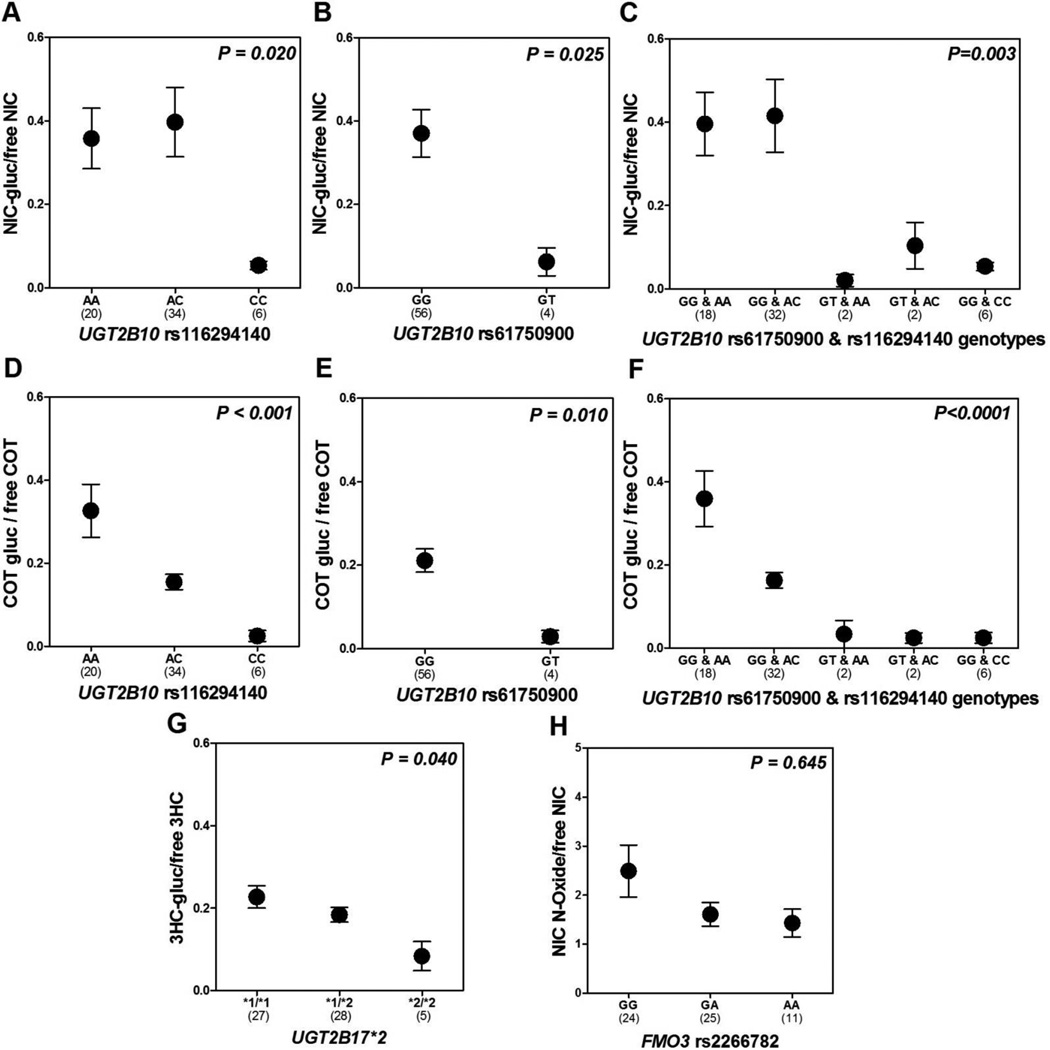
Figure 1.
Mean ± SEM nicotine-glucuronide/free nicotine and cotinine-glucuronide/free cotinine ratios according to UGT2B10 rs116294140 genotype (A&D) and according to UGT2B10 61750900 genotype (B&E) is shown; Mean ± SEM 3HC-glucuronide/free 3HC ratio according to UGT2B17*2 genotype is shown in (G); Mean ± SEM nicotine N-oxide/free nicotine ratio according to FMO3 rs2266782 genotype is shown in (H). UGT2B10 rs116294140 and rs61750900 genotypes were combined in (C&F). Group 1 includes individuals who are wild type for both variants (n=18); group 2 includes individuals who are wild type for rs61750900 and heterozygous variant for rs116294140 (n=32); group 3 includes individuals who are heterozygous variant for rs61750900 and wild type for rs116294140 (n=2); group 4 includes individuals who are heterozygous for both variants (n=2); group 5 includes individuals who are wild type for rs61750900 and homozygous variant for rs116294140 (n=6). All P-values indicated were derived from Mann-Whitney U tests comparing UGT2B10 rs61750900 GG and GT genotypes, or Kruskal-Wallis tests comparing UGT2B10 rs116294140, UGT2B17*2, FMO3 rs2266782, and UGT2B10 rs116294140 and rs61750900 combined genotypes. Abbreviation: SEM, standard error of the mean.