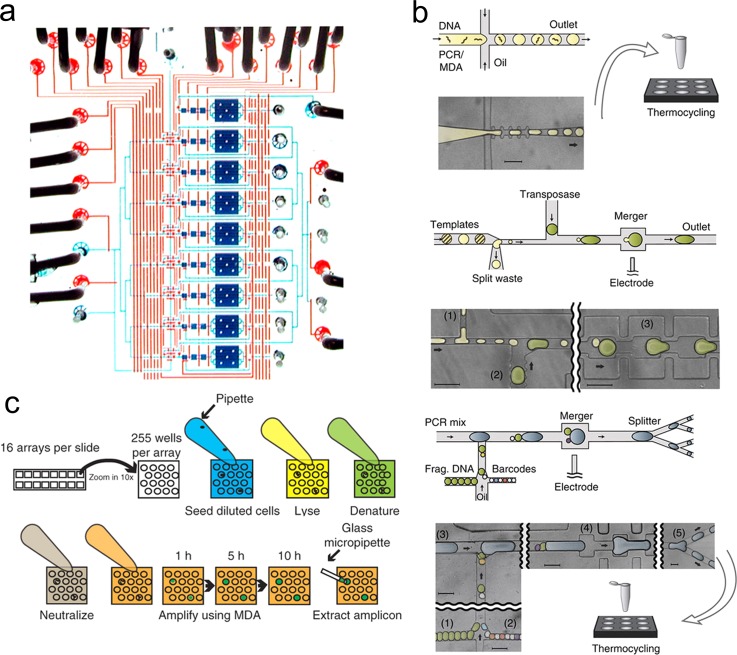
FIG. 3.
Microfluidic devices for MDA. (a) Micro-chamber MDA. A photograph of the single cell isolation and amplification chip. The fluidic chamber and channels are filled with blue dye and the control lines were filled with red dyes. Reprinted with permission from Marcy et al., PLoS Genet. 3(9), 1702–1708 (2007). Copyright 2007 PLOS. (b) Droplet MDA. The single cell is lysed in a tube and mixed with MDA reagents. The mixture is either directly used for conventional MDA or used to generate droplets in a microfluidic device. Reprinted with permission from Lan et al., Nat. Commun. 7, 11784 (2016). Copyright 2016 Macmillan Publishers Ltd. (c) Micro-well MDA (MIDAS). Each MIDAS chip contains 16 arrays of 255 micro-wells. The diluted cells are loaded in the microwells. Lysis solution, denaturing buffer, neutralization buffer, and MDA master mix are added to the microwells in sequence. The amplification procedure is monitored based on the growth of fluorescence. The amplicons are extracted for sequencing library construction. Reprinted with permission from Gole et al., Nat. Biotechnol. 31(12), 1126–1132 (2013). Copyright 2013 Macmillan Publishers Ltd.