Fig. 6.
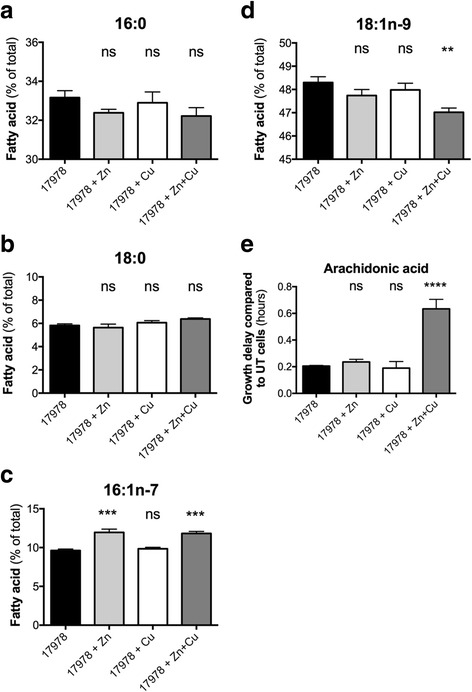
The effects of Zn and Cu on A. baumannii membrane biology. The major cellular fatty acid constituents of A. baumannii strain ATCC 17978, grown in the presence of 400 μM Zn, 400 μM Cu, 400 μM Zn + 400 μM Cu, or without added metal ions were determined by gas chromatography. The abundance of fatty acids, expressed as percentage of total cellular fatty acids, is (a) 16:0 (b) 18:0, (c) 16:1n-7 and (d) 18:1n-7. The data are the mean of at least biological triplicates (± SEM). Statistical analyses were performed by one-way ANOVA using Dunnett’s posttest; ns = not significant, ** = p < 0.01 and *** = p < 0.001. e The susceptibility of A. baumannii strain ATCC 17978 to arachidonic acid (20:4n-6) grown in the presence of 400 μM Zn, 400 μM Cu, 400 μM Zn + 400 μM Cu, or without added metal ions was determined by measuring the optical density at 600 nm (OD600). The growth delay between untreated and arachidonic acid-treated cells was examined by comparing the EC50 under each relevant metal ion stress condition. The data are the mean of at least biological triplicates (± SEM). Statistical analyses were performed by one-way ANOVA using Dunnett’s posttest; ns = not significant and **** p < 0.0001
