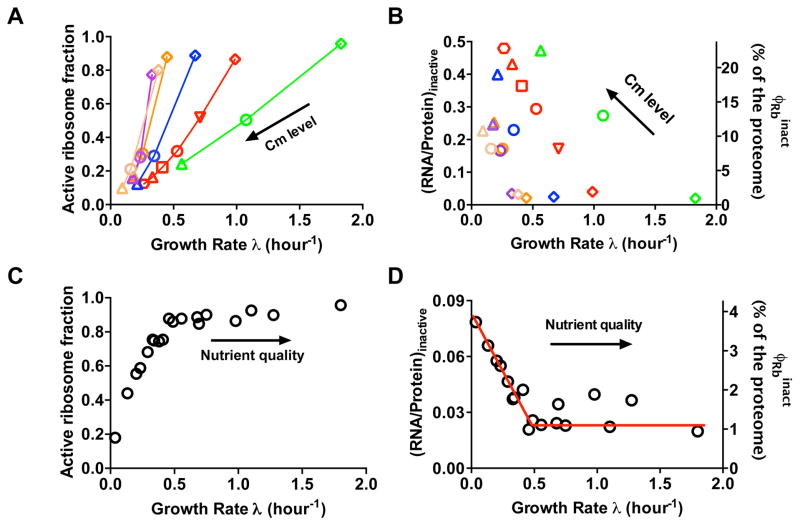
Figure 3. Growth-rate dependence of the active ribosome fraction.
(A) Growth-rate dependent fraction of active ribosome equivalent (factive) for cultures under sub-lethal doses of Cm, computed according to Eq. [N1.5] in Supplementary Note 1A. Symbol shapes and colors are the same as those shown in Fig. 2. Original data are given in Supplementary Table 6. (B) The absolute abundance of inactive ribosomes upon Cm inhibition. Left y-axis shows the portion of RNA-protein ratio (R/P) attributed to inactive ribosomes, given by (1 − factive) ×R/P, with R/P taken from Fig. 2B. Right y-axis shows the protein mass fraction of inactive ribosomes, as defined in Supplementary Note 1A. (C) Growth-rate dependent fraction of active ribosome equivalent (factive) under nutrient limitation. Original data are given in Supplementary Table 7. (D) The absolute abundance of inactive ribosomes upon nutrient limitation. The left and right y-axis are the same as those defined in Panel B, with R/P taken from Fig. 1D. The red line, showing a constant from moderate to fast growth range (λ>0.5/h) together with a linear relation between with growth rate at slow growth range ((λ<0.5/h), is shown to guide the eyes. Note that the error in the estimates, of factive arising from errors in ER and R/P values, is ~10%. Data shown in panel A to D are calculated based on the ER and R/P data (each with at least three replicates) shown in Fig. 1 and Fig. 2, respectively.