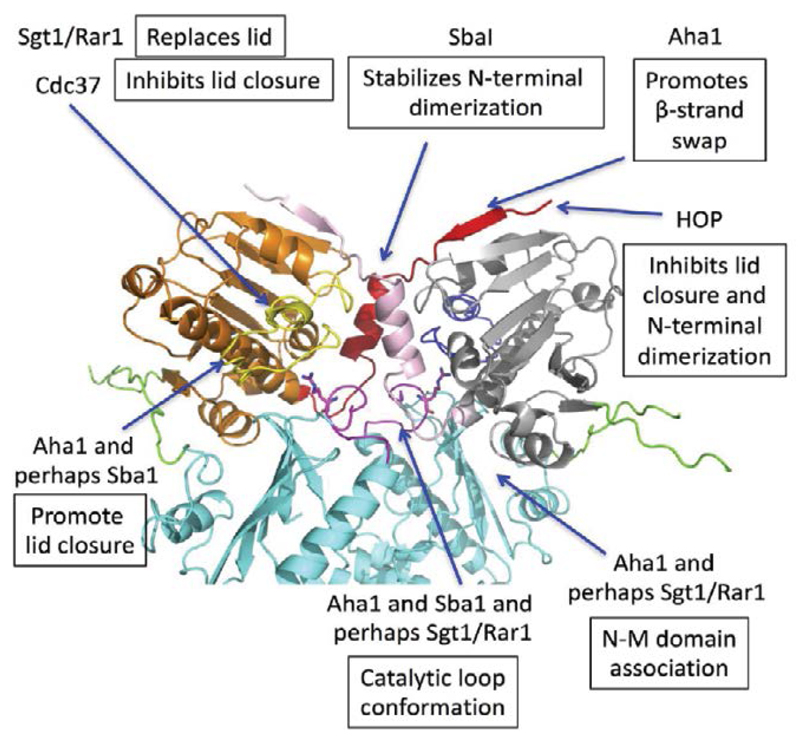
Figure 3.
Points of co-chaperone action on structural elements of Hsp90 essential for its ATPase activity. Cdc37p50 prevents molecular rearrangement of the lids of Hsp90. HOP may prevent lid closure and N-terminal dimerization probably by interacting with the N-terminal segments of Hsp90. Aha1 appears to interact with all the structural elements leading to a co-operative N-terminally dimerized state of Hsp90. Sba1 can stabilize Hsp90 complexes by reducing the ATPase activity of Hsp90 and it appears to interact with both the lid and N-terminal domains of Hsp90. Sba1 may also modulate the middle domain catalytic loop. Sgt1-Rar1 complex, appear to activate Hsp90 in an open state and convert it to a stable ADP-bound state.