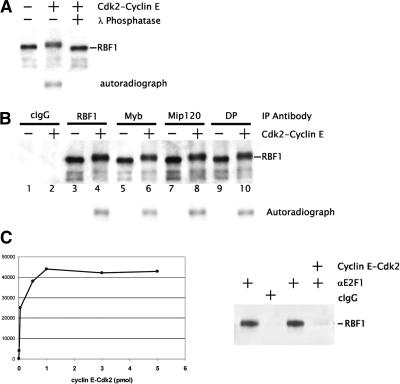
Figure 6.
Cdk phosphorylated RBF1 does not dissociate from the Myb-MuvB complex. (A) Flag-Mip130-purified proteins were incubated with purified recombinant Cyclin E-Cdk2. Immunoblot analysis using anti-RBF1 antibodies as indicated showed that the mobility of RBF1 was retarded in SDS-PAGE upon phosphorylation. Incubation with λ-phosphatase restored the normal mobility of the RBF1 protein. Incubation with 32P-autoradiographs indicated that RBF1 was phosphorylated in the presence of cyclin-Cdk. (B) Immunoprecipitations of Flag-Mip130 proteins were performed after mock (odd lanes) or Cyclin E-Cdk2 phosphorylation (even lanes). Shown is an anti-RBF1 immunoblot analysis performed after immunoprecipitation with the various antibodies indicated on the top. The presence of phosphorylated RBF1 is indicated by the autoradiograph. (C) A titration of the Cyclin E-Cdk2 levels was performed using a constant amount of purified Myb-MuvB complex. PhosphorImager analysis indicated that the RBF1 phosphorylation levels plateaued at the kinase concentration used in the experiments (3 pmol Cyclin E-Cdk2). (D) E2F1/RBF1 was immunoprecipitated from 0- to 12-h Drosophila embryo nuclear extract. The immunoprecipitated complex was washed and equilibrated with the kinase reaction buffer. Following immunoprecipitation using either anti-E2F1 or control nonspecific IgG, the pellet was washed and incubated for 30 min at 30°C with Cyclin E-Cdk2. Shown is an immunoblot analysis using anti-RBF1 antibodies in which Cylin E-Cdk2 treatment dirupts the interaction of E2F1 with RBF1.