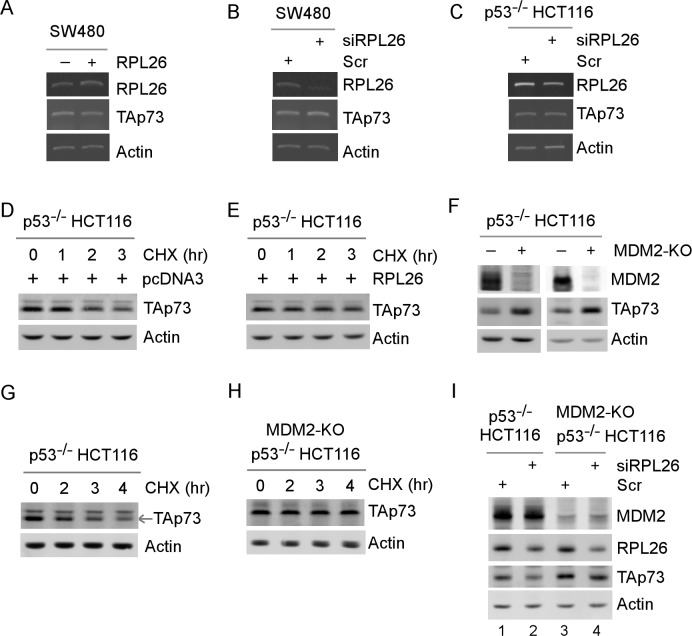
Figure 2. RPL26 modulates TAp73 protein stability in part via MDM2.
A. The levels of RPL26, TAp73 and actin transcripts were measured in SW480 cells, which were transfected with an empty vector or a vector expressing RPL26 for 48 h. B.-C. The level of RPL26, TAp73 and actin transcripts was measured in SW480 cells B. or p53−/− HCT116 cells C., which were transfected with scrambled siRNA or siRNA against RPL26 for 72 h. D.-E. The half-life of TAp73 protein was determined in p53−/− HCT116 cells, which were transfected with an empty vector D. or a vector expressing RPL26 E. for 48 h along with treatment of cycloheximide for various times. F. The levels of MDM2, TAp73 and actin proteins were measured in p53−/− HCT116 and MDM2-knockout p53−/− HCT116 cells. G.-H. The half-life of TAp73 protein was determined in p53−/− HCT116 and MDM2-knockout p53−/− HCT116 cells treated with cycloheximide for various times. I. The levels of MDM2, RPL26, TAp73 and actin proteins were measured in p53−/− HCT116 and MDM2-knockout p53−/− HCT116 cells, which were transfected with scramble siRNA or RPL26 siRNA as indicated for 72 h.