Figure 3. AZD feeding ameliorates 127Q (polyQ) induced eye defect and vision in the fruit fly.
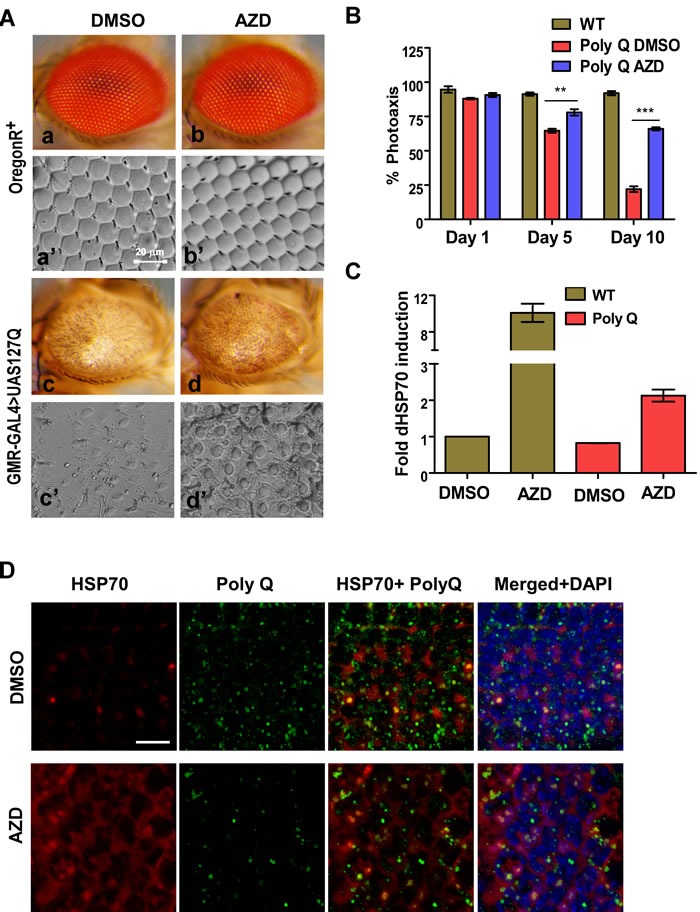
A. Dietary supplementation of AZD improved eye morphology and structure of ommatidial arrays (a-c' vs. b-d') damaged by polyQ expression. B. AZD supplementation significantly improved the vision defect caused by polyQ expression in the fly eyes as determined by phototaxis assay. Shown are the proportion (% on Y-axis; N = 75 flies in each case) of wild type and polyQ expressing flies (as indicated on the top) moving to the illuminated chamber on different days (X-axis; ** and *** indicate P < 0.01 and < 0.001), respectively, for comparison between DMSO and AZD treated polyQ flies. C. Dietary supplementation of AZD induces levels of HSP70 transcripts (Y-axis) in the head of the flies not expressing or expressing polyQ (X-axis). Data are mean±SEM, n ≥ 3. D. Compared to DMSO (upper row) dietary supplementation of AZD induces expression of HSP70 and reduces the level of polyQ in retinal cells as detected by immunostaining as indicated. Individual or merged staining in the confocal projection images are indicated on top of each column. Scale bar 20 micrometer.
