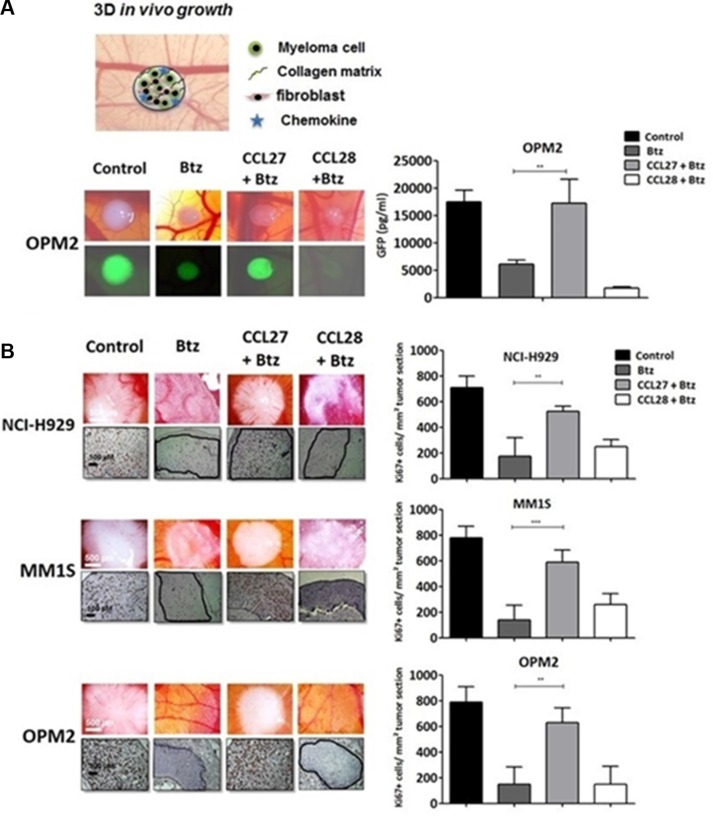
Figure 3. CCL27 rescues myeloma cells from bortezomib-induced cell death in a xeno-transplanted model.
(A) Chicken chorioallantoic membrane assay was used for in vivo testing and the setup of the 3D-onplant is summarized in the drawing. Tumor onplants containing myeloma cells and primary fibroblasts in a ratio of 11:1, bortezomib (1 nM) and/or chemokine (CCL27: 7.9 nM, CCL28: 8.1 nM) in a collagen matrix were positioned on the membrane and incubated for 5 days. Single myeloma xenografts were photographed using a stereo-fluorescence microscope (Olympus SZX10 at 12× magnification), excised, and GFP concentrations of single tumors were measured by Elisa. Values are shown as mean concentration in pg/ml ± SEM (n = 12). (B) Immunohistochemical analysis of cross-sections of NCI-H929, MM.1S and OPM-2 grafts in the chorioallantoic membrane model including control with and without bortezomib, CCL27 or CCL28 at the above mentioned concentrations; sections were stained with an anti-human Ki-67 antibody to detect growing myeloma cells. Pictures were taken using Zeiss Axiovert 200 M microscope at 200× maginification. The amount of Ki67 positive cells/tumor area are summarized in the graphs. **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001.