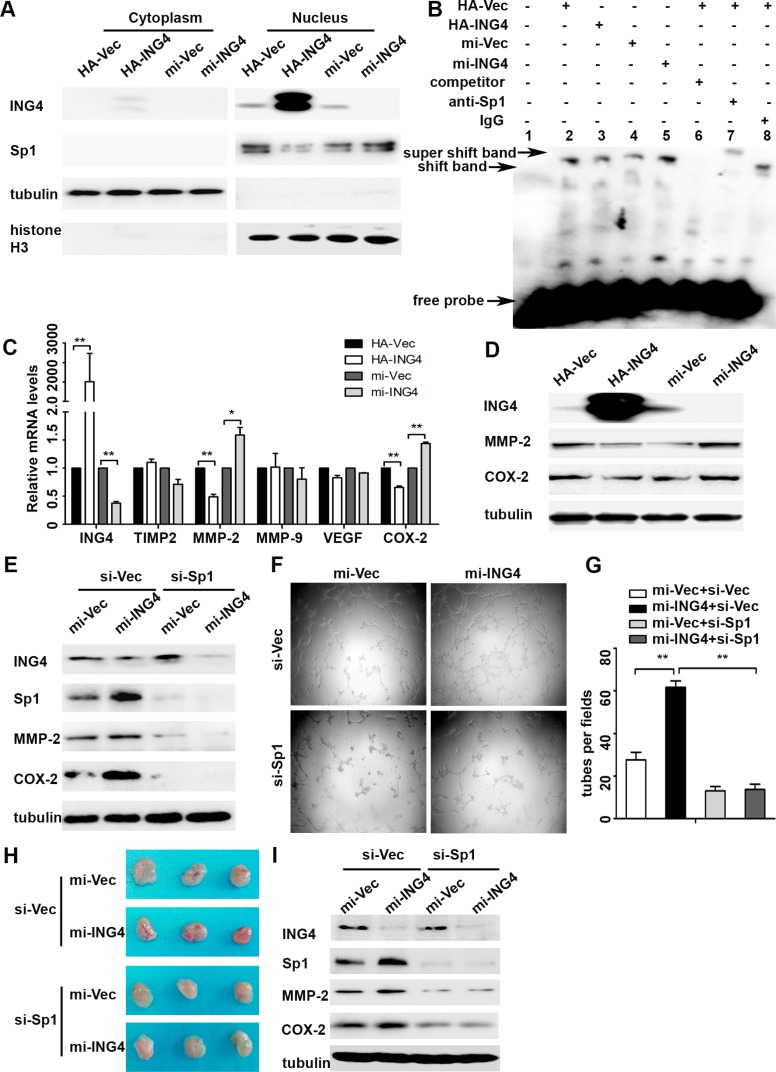
Figure 3. ING4 suppressed Sp1 expression and transcriptional activity to regulate expressions of its target pro-angiogenic genes MMP-2 and COX-2 and angiogenesis in vitro and in vivo.
(A) Western blot confirmed that ING4 inhibited the expression of nuclear Sp1. (B) ING4 altered the DNA affinity of Sp1. EMSA was performed using nuclear protein extracts from p53+/+HCT116 transfected with ING4 overexpression (HA-ING4), knockdown (mi-ING4) and respective controls plasmids (HA-Vec and mi-Vec). Lane 1 contains no nuclear extracts. All other lanes contain 1μg nuclear extracts. Lane 6 represents competition analysis using 100-fold unlabeled Sp1 probes. The super shift band was observed when the Sp1 antibody was added (lane 7) and IgG was used as negative control for super shift (lane 8). (C–D) Real time PCR and western blot were used to explore the expressions of Sp1 downstream pro-angiogenic genes MMP-2 and COX-2 in ING4 over-expressed, knocked down and control p53+/+HCT116 cells. (E) The increased expressions of MMP-2 and COX-2 by ING4 knockdown were abolished by Sp1 siRNA (si-Sp1). (F) Conditioned medium was collected and applied in tube formation. (G) Numbers of complete tubular structures formed by HUVECs were counted for ING4 knockdown, Sp1 knockdown or co-knockdown and control groups in p53+/+HCT116 (n = 3/group). (H) Photographs of matrigel plugs with ING4 knockdown, Sp1 knockdown or co-knockdown and control p53+/+HCT116 cells excised from mice after 10 days of growth in vivo. (I) The expressions of ING4, Sp1, MMP-2 and COX-2 were examined by western blot in matrigel plugs containing ING4 knockdown, Sp1 knockdown or co-knockdown and control p53+/+HCT116 cells. Data are presented as means ± standard deviations. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.001 (Student's t-test).