Figure 5. Functional characterization of proline hydroxylation pathway on Brd4 transcriptional activities and cell proliferation in MV4;11 cells.
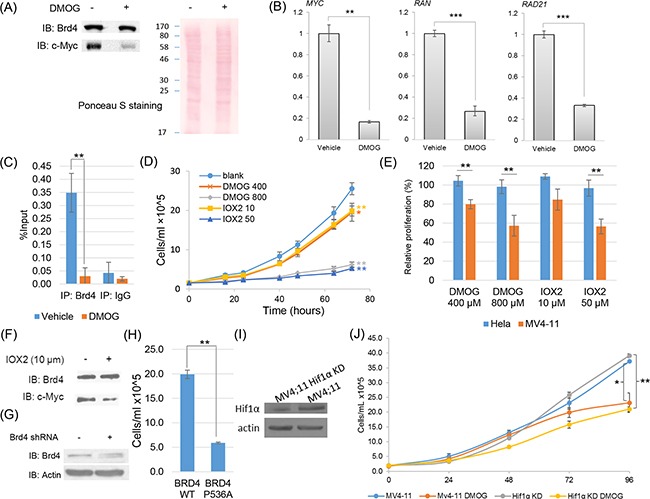
A. Western blotting analysis showing that the DMOG treatment of MV4;11 cells (800 μM, 24 hrs) significantly decreased the protein abundance of c-Myc. B. Quantitative real-time PCR analysis showing that the DMOG treatment of MV4;11 cells significantly decreased the transcriptional expression of known Brd4-targeted genes. C. Chromatin immunoprecipitation and quantitative PCR (ChIP-qPCR) analysis of Brd4 binding to the c-Myc promoter in MV4;11 cells with or without DMOG treatment. D. Cell proliferation assay of MV4;11 cells under control, DMOG and IOX2 treatment. Statistical analysis was performed between treated and control cells at 72 hrs. E. The relative proliferation of Hela and MV4;11 cells under DMOG (400 μM, 800 μM) and IOX2 (10 μM, 50 μM) treatments for 24 hrs comparing to the vehicle-treated control. F. Western blotting analysis showing that IOX2 treatment (10 μM, 16 hours) significantly decreased the protein abundance of c-Myc. G. Cell proliferation assay of MV4;11 cells with shRNA knockdown of endogenous Brd4 and expression of WT Brd4 and Brd4 with P536A mutation. H. Western blotting analysis showing that HIF1α was significantly knocked down in a stable MV4;11 cell line. G. Cell proliferation assay demonstrating that the growth of MV4;11 cells with and without HIF1α knocked down were both strongly inhibited by DMOG treatment (400 μM). All statistical analysis were performed with three biological replicates (Student's t-test, * p<0.05, ** p<0.01).
