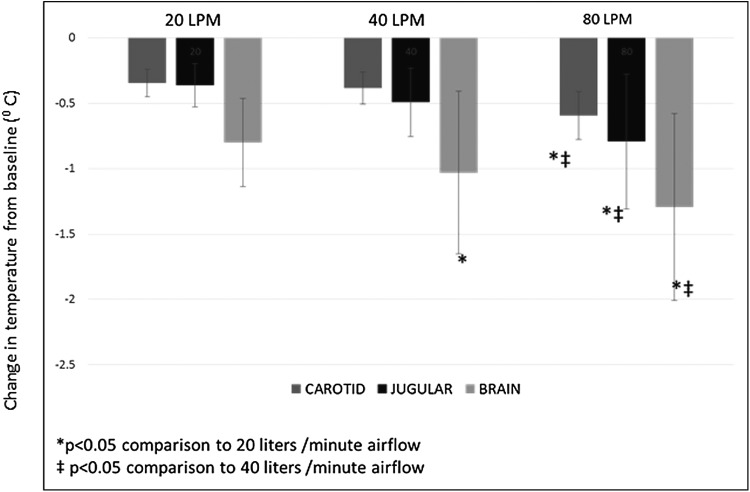
FIG. 2.
Effect of airflow rate on brain, jugular vein, and carotid artery temperature. Shown in the figure is the decrease in brain, jugular, and carotid temperatures from baseline values over a 10-minute exposure to 20, 40, and 80 LPM. The decrease in brain temperature was airflow dependent with greater cooling at higher airflow rates. Rates of jugular and carotid cooling were also higher between flow rates of 40 and 80 LPM.