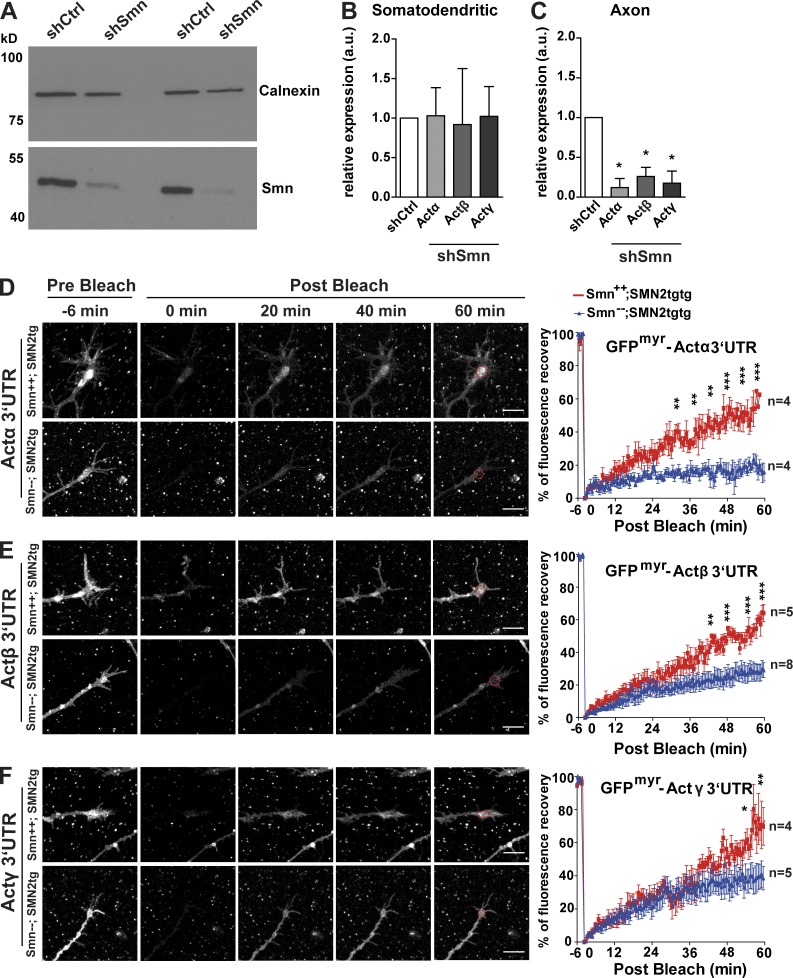
Figure 10.
Axonal transport and translation of Actα, Actβ, and Actγ mRNAs are impaired in Smn-deficient motoneurons. (A) Immunoblot shows reduction in Smn protein levels in motoneuron lysates after shRNA-mediated knockdown of Smn. Calnexin was used as loading control. A Western blot from two independent knockdown experiments is shown (representative for n = 3). (B) shSmn transduced motoneurons were plated in microfluidic chambers, and RNA was extracted and analyzed by quantitative RT-PCR. mRNA levels of actin isoforms are not altered in the somatodendritic compartment. (C) Axonal mRNA levels of all three actin isoforms are reduced in Smn-depleted neurons (*, P < 0.021 for Actα; *, P < 0.013 for Actβ and Actγ for n = 4). Statistical analysis was done using a one-tailed Mann-Whitney test. (D–F) On the left are representative time-lapse images of FRAP sequences of growth cones of motoneurons isolated from type I SMA mice transduced with eGFPmyr-Actα3′UTR (D), eGFPmyr-Actβ3′UTR (E), and eGFPmyr-Actγ3′UTR (F). (D) The graph on the right shows a reduction in fluorescence recovery of Actα reporter in Smn−−; SMN2tgtg compared with Smn++; SMN2tgtg neurons (**, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001). (E, right) Fluorescence recovery of Actβ reporter is reduced in Smn-deficient neurons (**, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001). ROIs are indicated in red circles. (F, right) Differences in recovery of Actγ reporter become apparent after 54 min after bleach (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01). Statistical analysis in D–F was done using a two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc test. Shown are mean ± SEM. Bars, 10 µm.