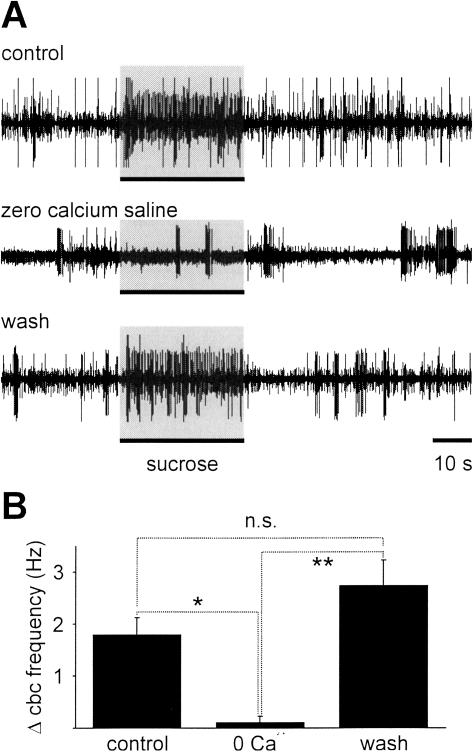
Figure 5.
Response of cerebral-buccal connective to lip application of sucrose is blocked by zero calcium saline, suggesting that it is mediated by chemical synapses in the cerebral ganglia. (A) Sample records from a cut cerebral-buccal connective showing responses to sucrose (0.02 M, 30 sec) applied to the lips in normal saline (top trace), in nominally zero calcium saline (middle trace), and after return to normal saline (bottom trace). Note the reduced levels of spontaneous activity and the lack of an obvious response to sucrose application in zero calcium saline. (B) The summary of average changes in cerebral-buccal connective activity during the period of sucrose application shows that zero calcium saline applied to the cerebral ganglia completely abolishes the sucrose response in the cerebral-buccal connective (one-way ANOVA for correlated samples, P < 0.01 followed by post-hoc Tukey HSD tests, control versus zero calcium: P < 0.05, zero calcium versus wash: P < 0.01; n = 6 preparations).