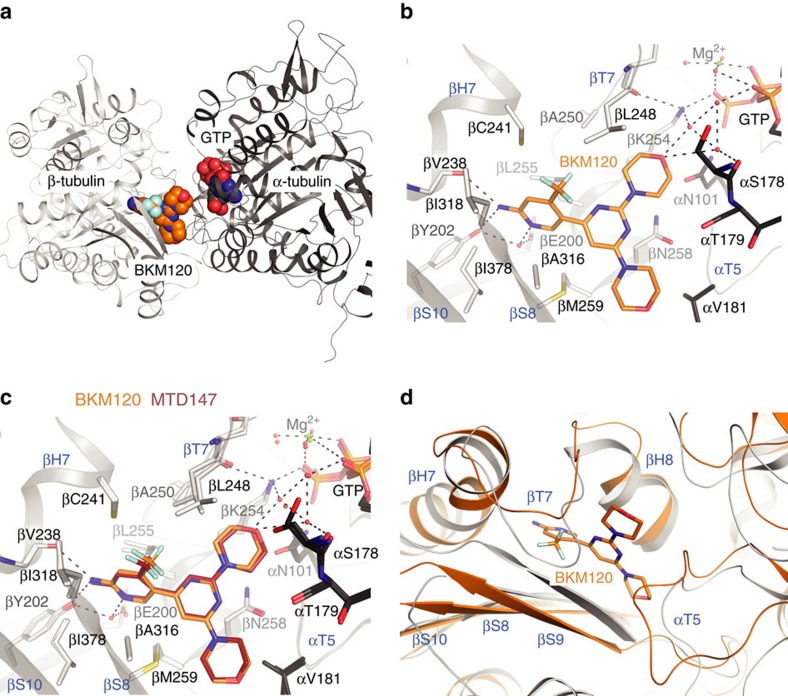
Figure 3. Interactions of BKM120 and derivatives with tubulin.
(a) Backbone of the αβ-tubulin heterodimer (in cartoon representation) in complex with BKM120; GTP is shown in spheres representation (PDB ID 5M7E). (b) BKM120 binding site in tubulin. Relevant amino acids are labelled in single letter code; secondary structure elements (marine blue) are H: helix; S: β-sheet; T: T-loop, preceeded by the respective tubulin subunit, α or β. Resolved water molecules are indicated as red spheres; dashed lines denote hydrogen bonds or interactions discussed in the main text. (c) Overlay of BKM120 and MTD147 (PDB ID 5M7G) binding to the colchicine-binding pocket of tubulin in the T2R-TTL complex. None of the compounds affected the global conformation of tubulin in the complex (rmsd 0.290 Å; 1941 Cα atoms) compared to the non-ligated T2R-TTL complex (PDB ID: 4I55, refs 12, 13). Residues of strands βS8 and βS9, loop βT7 and helices βH7 and βH8 of β-tubulin and of loop αT5 of α-tubulin form the boundaries of the binding site. For all investigated compounds, the trifluoromethyl substituted α-aminopyridine moiety pointed into the hydrophobic pocket outlined by side chains of βCys241, βLeu248, βAla250, βAla316, βIle318 and βAla354, with its amino group in H-bond distance to the βTyr202 OH and the βVal238 backbone carbonyl. The ring nitrogen is in H-bond contact to βGlu200 and βTyr202 through a water molecule. One morpholino group points towards the nucleotide-binding site, with the ether oxygen connected to two water molecules that establish an H-bond network to the side chains of Asn101 of α-tubulin, to Lys254 of β-tubulin, to the alpha and gamma-phosphates of the nucleotide and to the backbone carbonyl of Ser178 of α-tubulin. (d) Overlay of the BKM120 binding region in αβ-tubulin in the context of a microtubule (‘straight' tubulin conformation, grey; PDB ID: 1JFF35) and in αβ-tubulin bound to BKM120 (orange).