Figure 3.
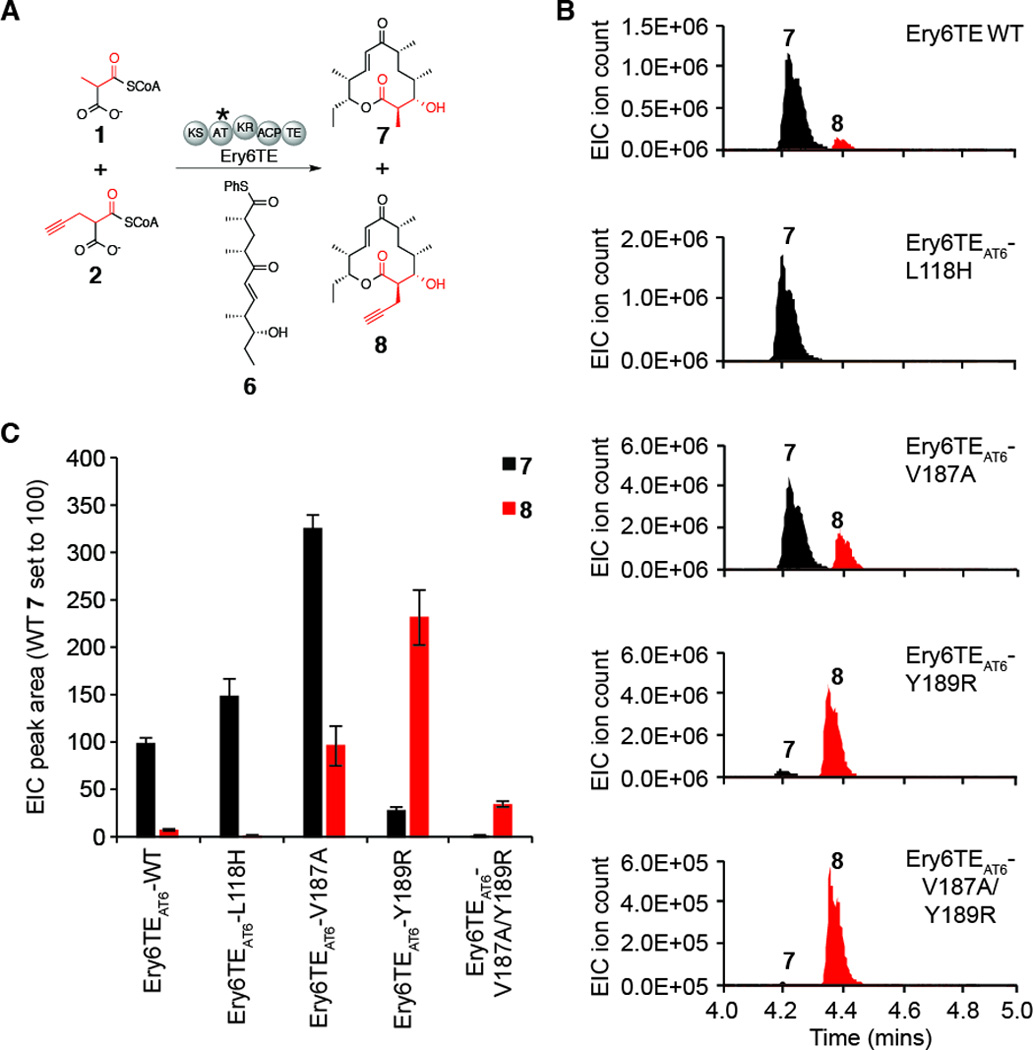
Extender unit selectivity of wild-type and mutant Ery6TEs using equimolar concentrations of natural and non-natural extender units. (A) Scheme illustrating the competition assay to report extender unit selectivity. Asterisk indicates domain location of mutations. (B) Extracted ion chromatograms (EIC) of Ery6TE-catalyzed chain extension reactions (7 [M-H2O+H]+ m/z = 279.1955; 8 [M-H2O+H]+ m/z = 303.1955). (C) Product distribution of wild-type and mutant Ery6TE (values are mean EIC peak area ± SD; n = 3; wild-type production of 7 set to 100).
