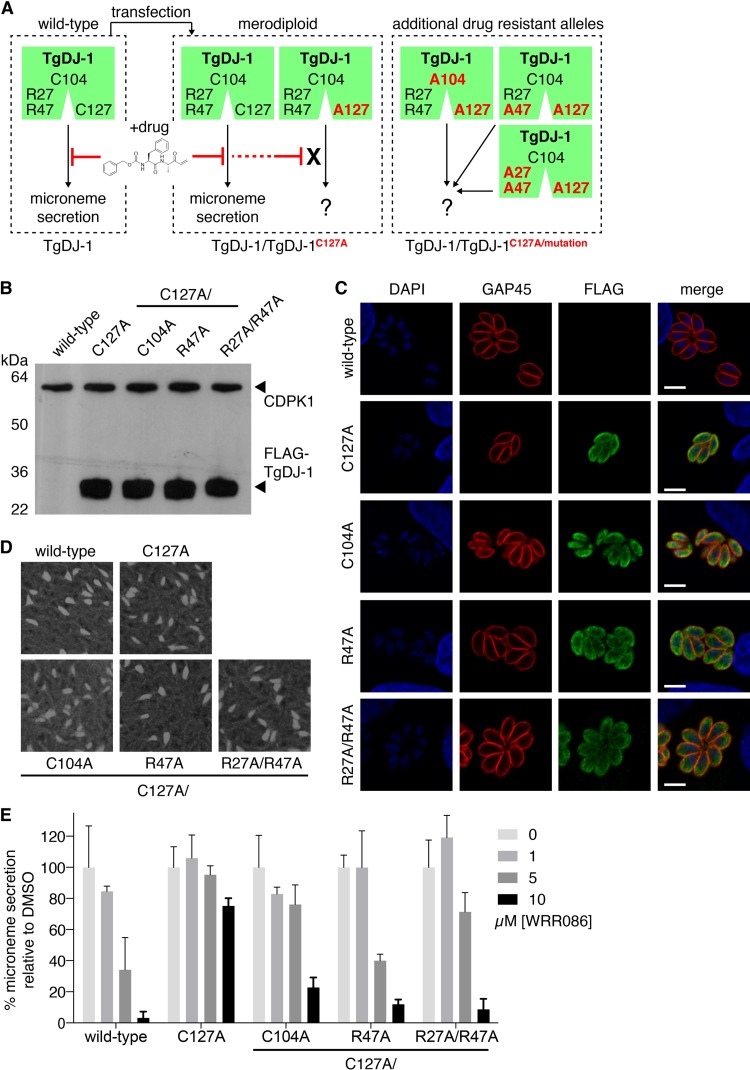
FIG 6 .
Engineered drug-insensitive TgDJ-1 alleles confirm the functional contribution of the TgDJ-1/CDPK1 complex to microneme secretion. (A) Schematic of the strategy to engineer and introduce drug-insensitive alleles to generate merodiploid parasite strains. (B) Western blot analysis using both anti-CDPK1 and anti-FLAG antibodies for expression of CDPK1 and FLAG-tagged TgDJ-1 in isogenic parasite strains expressing either TgDJ-1C127A (C127A), TgDJ-1C127A/C104A (C104A), TgDJ-1C127A/R47A (R47A), or TgDJ-1C127A/R27A/R47A (R27A/R47A). This nomenclature for the merodiploid parasites is used throughout. (C) Indirect immunofluorescence assays examining the localization of intracellular TgDJ-1 merodiploid parasites. Gliding-associated protein 45 (GAP45) is used as a marker for the inner-membrane complex/plasma membrane; DAPI, nuclear stain. Scale bar = 5 µM. (D) Plaque assays comparing growth of wild-type and TgDJ-1 merodiploid parasites. (E) Quantification of Western blot analysis of induced microneme secretion assays performed in the presence of a titration of WRR-086. Data represent means ± SD for n = 3 experiments. Significance was calculated for a two-way ANOVA statistical analysis comparing wild-type and all merodiploid strains. Significance for comparison of the different strain group means = **** (P ≤ 0.0001); and the different WRR-086 concentrations (0, 1, 5, 10 µM) = **** (P ≤ 0.0001). Post-hoc pairwise comparison of the different strains for each WRR-086 concentration was performed using Tukey’s multiple comparison test and the data presented in Table S3.