Figure 1. Recombineering strategy used to produce 129S-Cdh23c.753A and B6-Cdh23c.753G SNV mice.
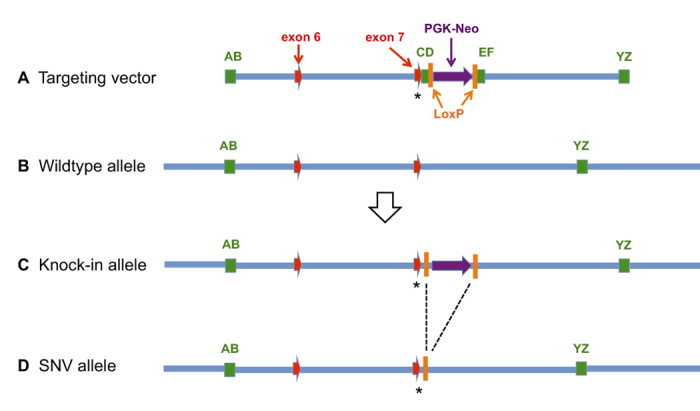
To produce B6N strain mice with the Cdh23c.753G SNV, a targeting vector with DNA from a 129S1/Sv BAC clone was constructed for recombination with C57BL/6 N ES cells (JM8.A3). To produce 129S strain mice with the Cdh23c.753A SNV, a targeting vector with DNA from a C57BL/6 J BAC clone was constructed for recombination with 129S1/SvImJ ES cells. (A) Targeting vector: The Cdh23 targeted region (9,729 bp) was cloned into a linearized pBlight plasmid (4695 bp) by retrieval from a BAC clone with AB (300 bp) and YZ (320 bp) homology arms. PGK-Neo and LoxP sites then were inserted into the plasmid by retrieval from a synthesized DNA cassette (2320 bp) with CD (200 bp) and EF (203 bp) homology arms. The targeted Cdh23c.753 SNV (marked by asterisk) is separated from the cassette insertion site by 142 bp and from PGK-Neo by 178 bp. In this figure, the targeted Cdh23c.753 SNV is shown as the last nucleotide of exon 7 according to Genbank transcript AF308939, which is equivalent to exon 9 in other transcripts such as NM_023370. (B) Wildtype allele: The targeted Cdh23 region of wildtype mouse genomic DNA showing positions of AB and YZ homology arms relative to exons 6 and 7. (C) Knock-in allele: After homologous recombination between the targeting vector and the wildtype Cdh23 allele, ES cells were selected for the presence of the PGK-Neo cassette and the closely linked targeted SNV (asterisk). Restriction enzyme cleavage sites and genomic probes (5′ and 3′) were used to distinguish wildtype and knock-in alleles. (D) The PGK-Neo cassette was subsequently removed by Cre-Lox recombination to produce the final SNV allele.
