Figure 4.
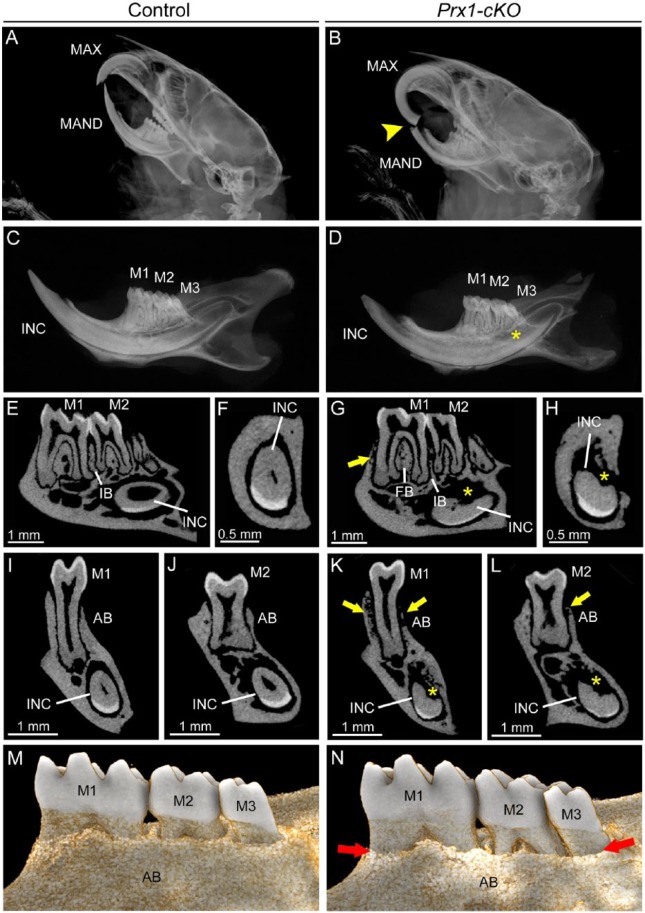
Mineralization defects in dentoalveolar tissues of Prx1-cKO mice. Dentoalveolar tissues were analyzed by radiography and micro–computed tomography (micro-CT) in WT control and Prx1-cKO mice (n = 3 per genotype) at 24 wk. Compared with (A) WT crania, radiographs of (B) Prx1-cKO mice show mandibular incisor fracture and malocclusion (yellow arrowhead) of maxilla (MAX) and mandible (MAND). Compared with (C) WT hemimandibles, radiographs indicate that (D) Prx1-cKO mice feature reduced mineralization of bone and incisor (INC), although molars (M1-M3) appear relatively normal. By micro-CT, well-mineralized structures of the (E, F, I, J) WT mandible are observed in (G, H, K, L) Prx1-cKO mandibles to be defective, especially radiolucent and reduced regions (yellow arrows) of alveolar bone (AB) and reduction in bone height in the furcation region (FB) and interproximal bone (IB) between molars. Lingual root analogs of incisor teeth are severely defective (yellow *). (M, N) Three-dimensional reconstructions of micro-CT scans reveal dramatically reduced lingual alveolar bone height (red arrows) in Prx1-cKO mice, exposing roots surfaces of M1 to M3. cKO, conditional knockout; WT, wild type.