Fig. 2.
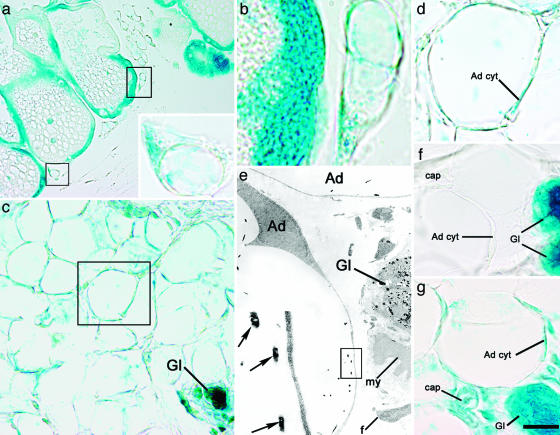
Postlactation adipocytes express the gene reporter driven by the alveolar epithelial cell-specific WAP promoter. (a–f) Mammary gland of WAP-Cre/R26R mouse, β-gal histochemistry. (a and b) On day 1 of postlactation involution, epithelial alveolar cells of the gland as well as adipocyte precursors (boxed) stain for X-Gal. (a Inset) Enlargement of the lower of the two boxed areas in a. (b) Enlargement of the upper of the two boxed areas in a. (c–e) On day 10 of postlactation involution, atrophic glands and most adipocytes are positive for X-Gal. (c) Gl, atrophic glands. (d) Enlargement of the area boxed in c. The cytoplasm of the adipocyte (Ad cyt) is X-Gal-positive. (e) By electron microscopy, typical X-Gal crystals are present only in adipocytes (Ad) and the epithelial component of the atrophic gland (Gl). Note the absence of crystals in other cell types. my, Myoepithelial cell; f, fibroblast. (e Inset) Enlargement of boxed area in e showing the typical crystals (arrows). (f) On day 9 of pregnancy, only the epithelial component of the mammary gland (Gl) is positive, whereas adipocytes (Ad cyt) and the other cell types [such as capillary (cap)] do not stain for X-Gal (negative control). (g) In a ROSA26 mouse (positive control) on day 1 of postlactation involution, all of the cell types found in the mammary gland were positive. Ad cyt, adipocyte cytoplasm; cap, capillary; Gl, gland. [Scale bar: 17 (a), 4 (a Inset), 2 (b), 9 (c), 4 (d, f, and g), 2 (e), and 0.4 (e Inset) μm.]