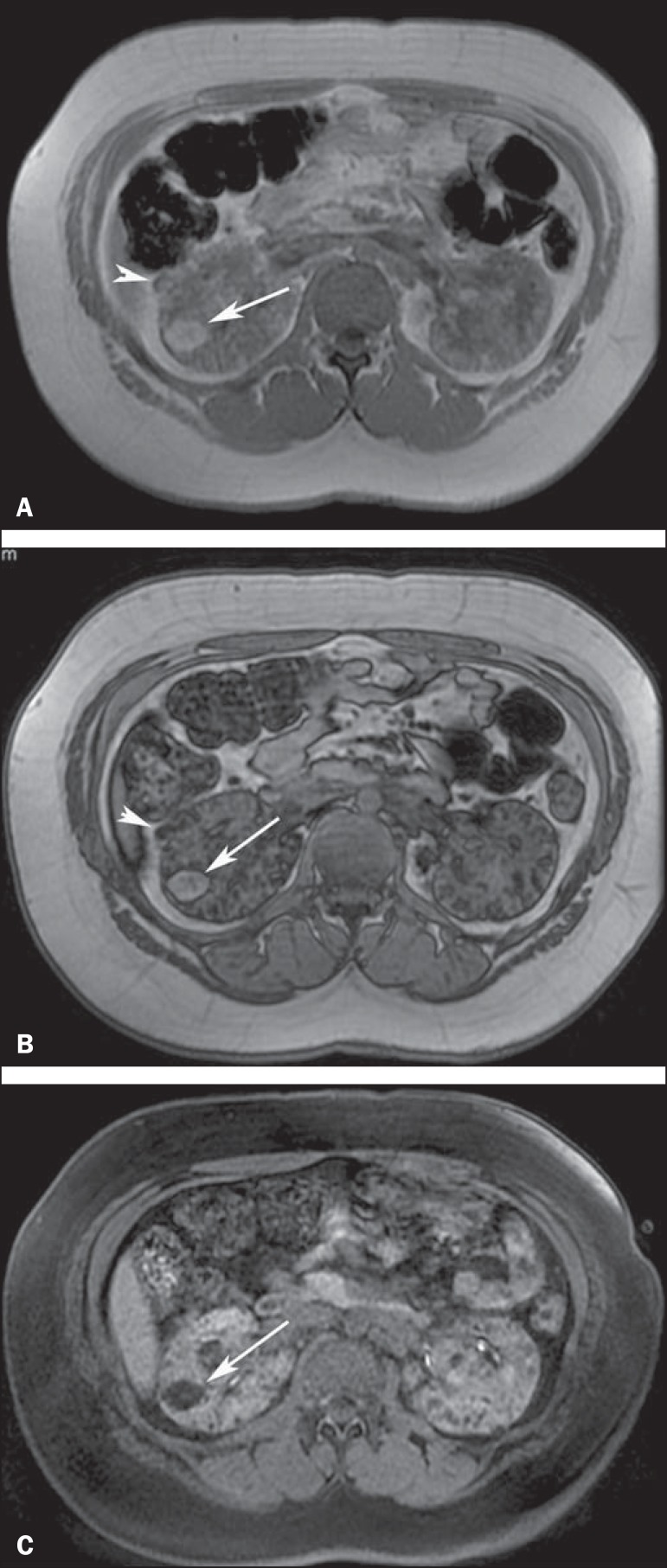
Figure 8.
A 21-year-old woman with tuberous sclerosis complex and multiple renal angiomyolipomas. T1-weighted in-phase gradient-recalled echo image (A) shows a hyperintense right renal mass (arrow). T1-weighted opposed-phase gradient-recalled echo image (B) shows a peripheral India ink artefact at the fat-water interface between the mass and surrounding normal renal parenchyma, a finding diagnostic of lipid-rich angiomyolipoma. T1-weighted fat-suppressed image (C) shows diffuse intralesional low signal intensity in the lipid-rich angiomyolipoma. Note also a lipid-poor angiomyolipoma in the right kidney, appearing as a hyperintense nodular lesion in (A) (arrowhead) and presenting homogeneous internal signal loss in (B) (arrowhead) due to the presence of microscopic amounts of fat within the lesion.