Fig. 1.
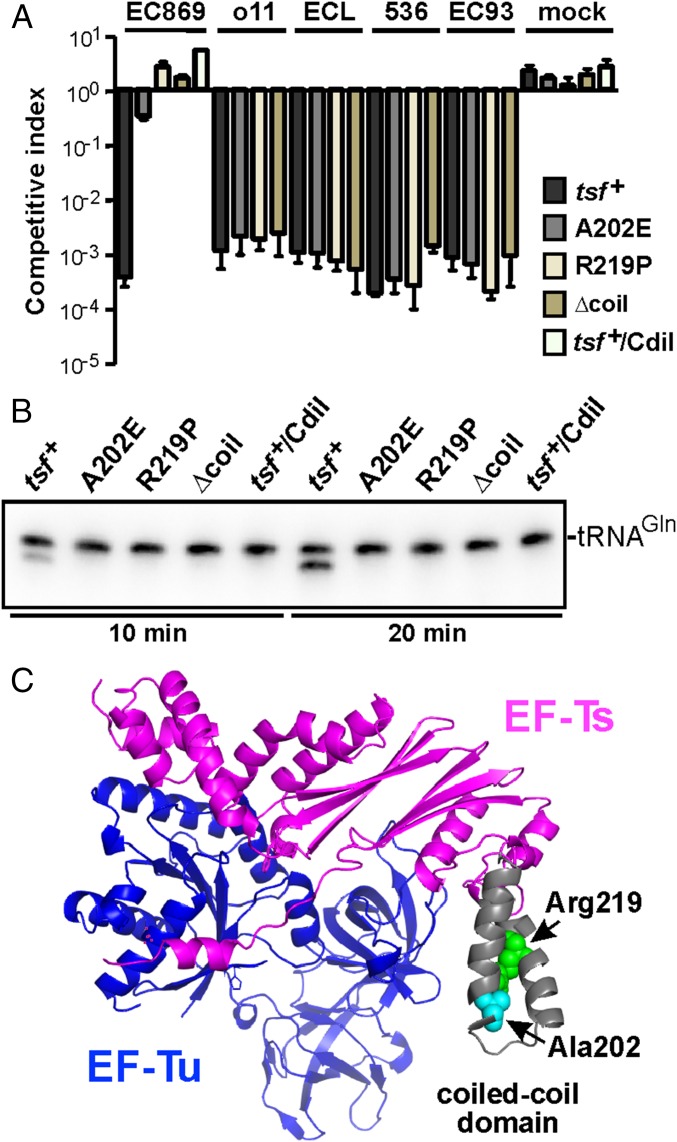
E. coli tsf mutants are resistant to CdiA-CTEC869. (A) E. coli MG1655 target strains carrying the indicated tsf alleles were cocultured with E. coli EPI100 inhibitor cells that deploy CdiA-CTEC869 (EC869), CdiA-CTo11EC869 (o11), CdiA-CTECL (ECL), CdiA-CTEC536 (536), or CdiA-CTEC93 (EC93) toxins. After 3 h, viable cell counts for each population were determined and used to calculate the competitive index as described in Materials and Methods. Mock inhibitors do not express a CDI system. Data are presented as averages ± SEM for three independent experiments. (B) E. coli EPI100 inhibitor cells expressing CdiA-CTEC869 were cultured at a 1:1 ratio with E. coli MG1655 target strains carrying the indicated tsf alleles. Total RNA was isolated after 10 and 20 min and subjected to Northern blot hybridization for tRNACUGGln. Because CDIEC869 inhibitor cells are immune to toxin activity, 50% substrate conversion is indicative of complete cleavage in target cells. (C) Structure of the E. coli EF-Tu·EF-Ts complex [Protein Data Bank (PDB) ID code 1EFU]. The locations of EF-Ts Ala202, Arg219, and the coiled-coil domain are indicated.