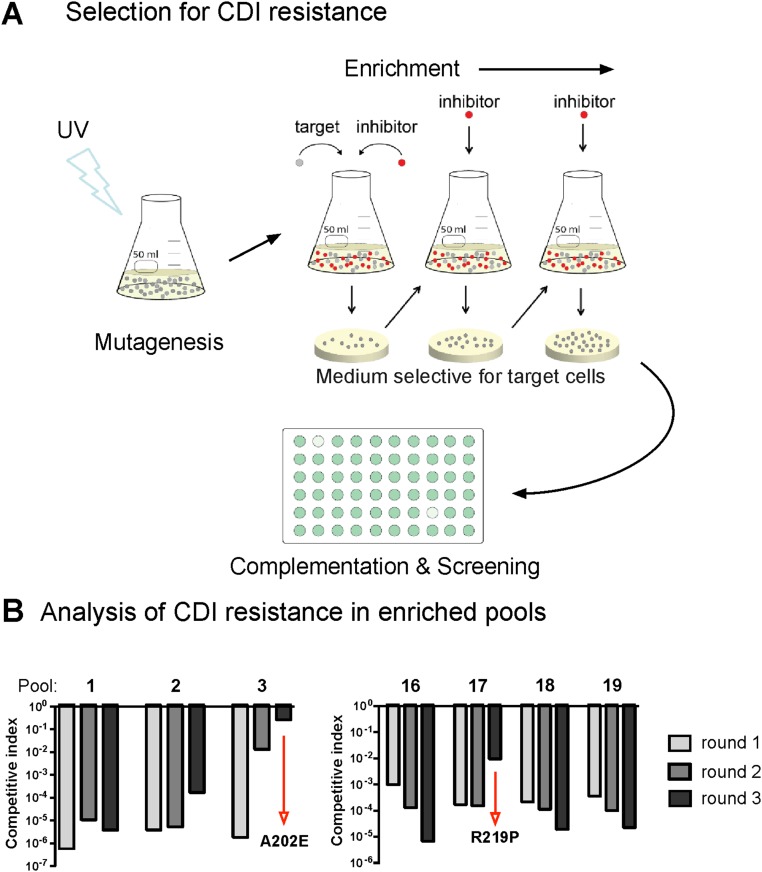
Fig. S1.
Selection of CdiA-CTEC869–resistant mutants. (A) Cultures of logarithmic growth-phase E. coli cells were UV-irradiated and cocultured at a 1:1 ratio with CDIEC869 inhibitor cells for 3 h. After three cycles of selection, target-cell clones from independent experiments were isolated and tested for CDI resistance. Complementation analysis was used to identify the gene(s) responsible for the CDIR phenotype. The CDIR mutant from pool 3 was labeled with GFP and transduced with a cosmid library of E. coli genomic DNA. Individual transductants were screened for CDIS in competition cocultures with CDIEC869 inhibitor cells in microtiter plates. Complementation to the CDIS phenotype results in low GFP fluorescence in competition well. (B) Pools of UV-irradiated target cells were mixed 1:1 with CDIEC869 inhibitor cells and cocultured for 3 h. CDIR mutants were selected with iterative cycles of competition coculture. Mutant pools containing CDIR target cells were identified by determining the competitive index for round of enrichment.