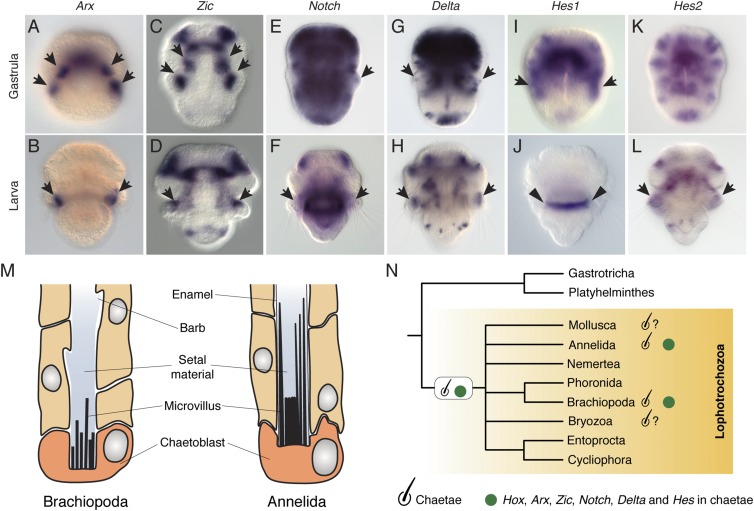
Fig. 6.
Expression of chaetae-related genes during T. transversa embryogenesis. (A–L) Whole- mount in situ hybridization of Arx, Zic, Notch, Delta, and two Hes genes in gastrula embryos and larvae of T. transversa. (A) In mid gastrulae, Arx is expressed in the ectoderm of the prospective chaetae sac territories (black arrows) and in a ventral domain. (B) In early larvae, Arx is expressed in the chaetae sacs (black arrows). (C) In late gastrulae, Zic is expressed in the mesoderm of the chaetae sacs (black arrows), apical lobe mesoderm, and anterior ectoderm. (D) In early larvae, Zic is detected in the chaetae sacs (black arrows), in a domain in the pedicle lobe, and in the anterior mesoderm and anterior ectoderm. (E and F) Notch is broadly expressed in the ectoderm and mesoderm of the late gastrula and early larva, particularly in a cluster of a few cells of the developing chaetae (black arrows). (G and H) Delta is strongly expressed in the apical lobe and in a salt and pepper manner in the mantle and pedicle lobe, including the chaetae (black arrows). (I and J) Hes1 is observed in the lateral ectoderm of the gastrula (black arrows), in the area that will subsequently form the chaetae and mantle lobe ectoderm. It is not detected in the larva. (Black arrowheads indicate background expression in J.) (K and L) Hes2 is detected in a salt and pepper manner in the ectoderm and mesoderm of the T. transversa embryo, and in the chaetae of the larva (black arrows). The images are dorsal views (except I and K), with the anterior pole at the top. (M) Morphological similarities between brachiopod and annelid chaetae. Drawing adapted with permission from ref. 84. (N) The shared morphological and molecular characters of chaetae in Brachiopoda and Annelida, together with the presence of chaetae-like structures (chaetae sign with a question mark) in the Mollusca and Bryozoa, support the homology of this lophotrochozoan novelty.