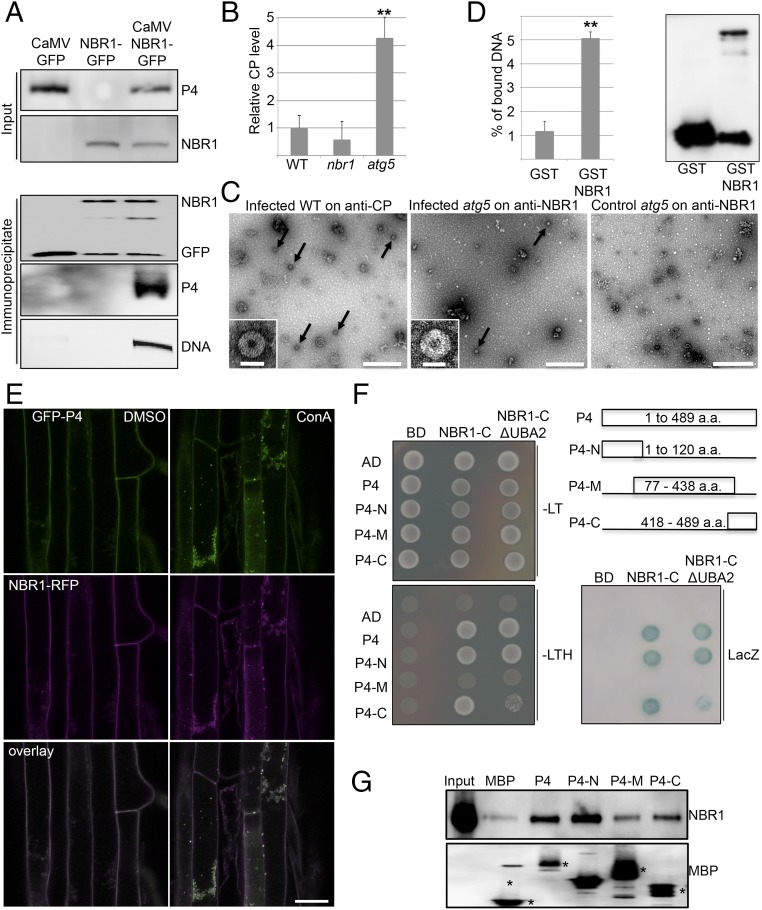
Fig. 3.
NBR1 binds to CaMV P4 and viral particles. (A) Presence of CaMV P4 in NBR1-GFP immunocomplexes from systemically infected transgenic plants. Immunoprecipitation was performed with anti-GFP monoclonal antibody; mock-treated NBR1-GFP as well as CaMV-infected GFP transgenic served as negative controls. Immunoblot analysis with anti-GFP and anti-P4 antibodies is shown for input and immunoprecipitated fractions, respectively, and viral DNA was detected by PCR using primers specific for the CaMV P1 movement protein. (B) Capture of CaMV P4 from lysates of infected WT, nbr1, and atg5 plants using anti-NBR1 antibody for coating and anti-P4 antibody for detection in a customized ELISA. Error bars represent SD (n = 3). (C) IC-TEM of CaMV particles (arrows) from infected WT and atg5 plants using anti-P4 and anti-NBR1 antibodies, respectively. Noninfected atg5 plants served as a negative control. (Scale bars, 500 nm.) Insets show enlargement of typical 50-nm particle structures. (Scale bars, 50 nm.) (D) In vitro pulldown of viral particles by the nonaggregating mutant GST-NBR1K11A. GST alone and GST-NBR1K11A were coupled to glutathione Sepharose and incubated with viral particles purified from infected nbr1 mutant plants. (Left) The amount of bound viral particles in eluates was quantified by qPCR of genomic DNA and is given as the percent relative to the input. (Right) Immunoblot analysis with anti-GST antibodies indicates the presence of GST proteins in eluates. (E) Colocalization of GFP-P4 and RFP-NBR1 in roots of transgenic Arabidopsis seedlings after treatment with DMSO and 0.5 μM ConA. Confocal images represent single planes of individual channels and the overlays. (Scale bar, 20 μm.) (F) Y2H-based interaction of P4 variants with the NBR1 C terminus that contains (NBR1-C) or lacks (NBR1-C ΔUBA2) the UBA2 and LIR domains. Yeast cells coexpressing P4, P4-N, P4-M, and P4-C as AD fusion and NBR1-C as BD fusion show growth on selective medium [without leucine and tryptophan (−LT) or without leucine, tryptophan, and histidine (−LTH)] and LacZ activity. Combinations with empty BD or AD vectors served as controls for auto-activation. The different P4 fragments and their amino acid coordinates are illustrated. (G) In vitro binding of GST-tagged NBR1K11A to MBP-fused P4 variants. MBP alone and MBP fusions were immobilized on agarose and incubated with recombinant GST-NBR1K11A protein. Immunoblot analysis of the eluates was performed with anti-NBR1 antibodies to indicate specific NBR1 binding (Upper) and with anti-MBP antibodies to demonstrate the amount of matrix-bound MBP proteins (asterisks) (Lower). Statistical significance (**P < 0.01) was revealed by Student’s t test (compared with WT in B and with GST in D).