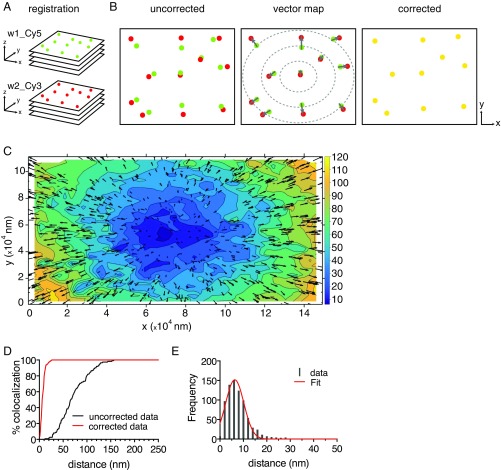
Fig. 1.
Super registration procedure for dual-color localization microscopy. (A) Registration. A poly–l-lysine–coated surface was sparsely loaded with 100-nm-diameter fluorescent beads, and z stacks were acquired in Cy5 (green) and Cy3 (red) channels with a wide-field microscope. (B) Chromatic aberration correction. Localization of the center of each spectrally separated PSF was determined by a Gaussian curve fitting using FISH_QUANT software (20); then all centroids were allocated in pairs, and distances were measured by using MATLAB custom algorithms (Materials and Methods and SI Results). A vector transformation map (affine transformation matrix) was used to then correct the images for chromatic aberration. Arrows illustrate displacement vectors. Yellow circles illustrate corrected images. (C) Objective contour distortion map of chromatic aberration. The actual distortion determined by the vector map in B for the specific objective used in this study. The entire FOV is represented (in nanometers). Vectors in black indicate chromatic shift direction and magnitude (Cy5 to Cy3). Cooler colors require minimal correction; warmer colors indicate major correction (in nanometers). (D) Percentages of colocalization between spectrally separated centroids before (black line) and after (red line) correction was applied to the entire FOV. (E) Distribution of observed distances of centroid pairs in two-color images after correction. Data are shown as gray bars, and the Gaussian fit is the red line. Mean of distribution = 7.86 ± 0.21 nm. Error, SEM.