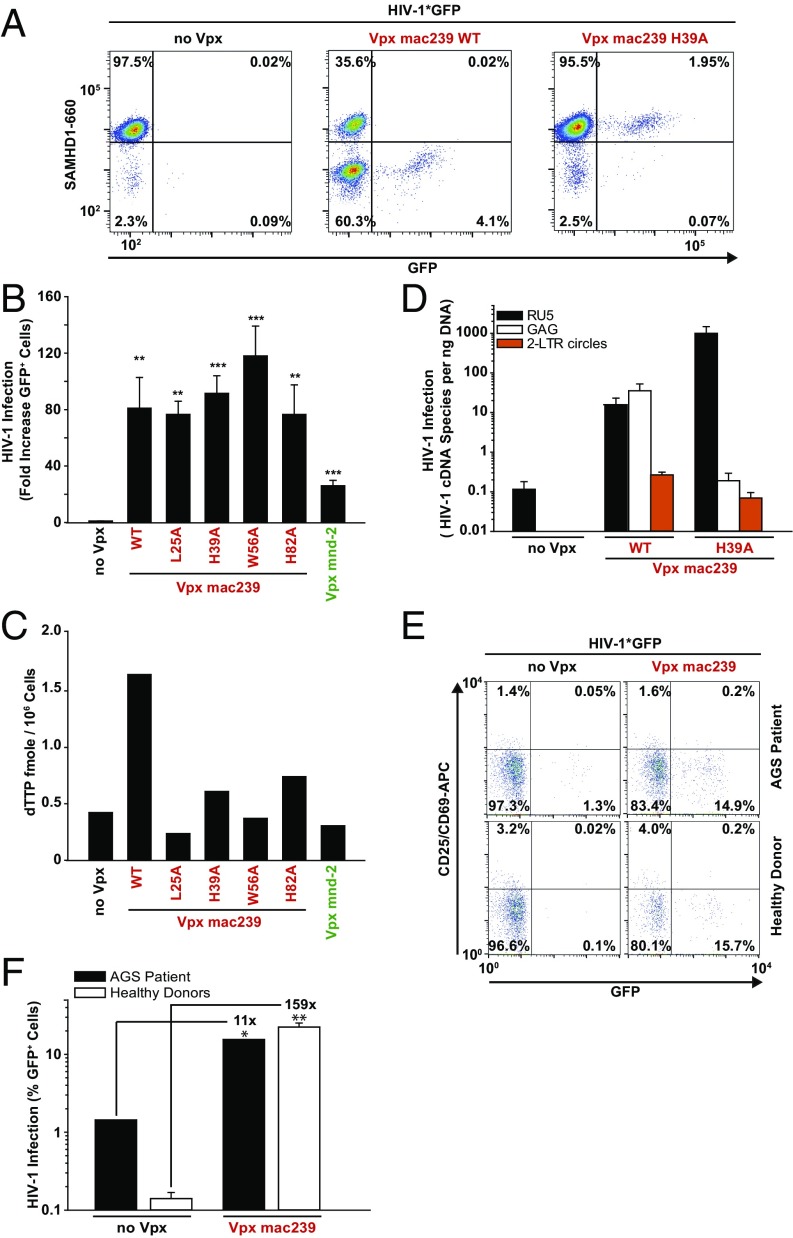
Fig. 4.
Antagonism of a SAMHD1-independent early postentry restriction for HIV-1 in resting CD4 T cells is a conserved feature of Vpx proteins. (A and B) Resting CD4 T cells from healthy donors were challenged with equivalent infectious units of X4 HIV-1*GFP virions without (no Vpx) or with incorporation of the indicated Vpx alleles and point mutants and analyzed 3 d later for GFP expression and SAMHD1 levels. (A) Dot plots of flow cytometric analysis of intracellular SAMHD1 and GFP levels for one representative donor. (B) Factor of increase of Vpx-mediated HIV-1 infection enhancement 3 d postchallenge. Shown are arithmetic means + SEM of data from at least three donors. (C) Resting CD4 T cells were cotransfected with pDisplay-YFP and expression constructs for the indicated Vpx constructs, sorted for YFP surface expression, and analyzed for dTTP levels. Shown are the arithmetic means from two independent experiments. (D) Resting CD4 T cells were challenged with equivalent infectious units of the indicated DNase-treated virus stocks and harvested 3 d later for qPCR analyses. Shown are levels of early (RU5) and late (GAG) RT products as well as 2-LTR circles presented as arithmetic means + SEM of five donors. (E and F) Resting CD4 T cells from a patient with AGS with SAMHD1 deficiency and from two healthy donors were challenged with equivalent infectious units of X4 HIV-1*GFP virions without (no Vpx) or with incorporation of Vpx from SIVmac239 and analyzed 3 d later for expression of GFP and activation markers CD25/CD69. (E) Representative FACS dot plots and (F) arithmetic means of the percentages of GFP+ cells of duplicate infections.