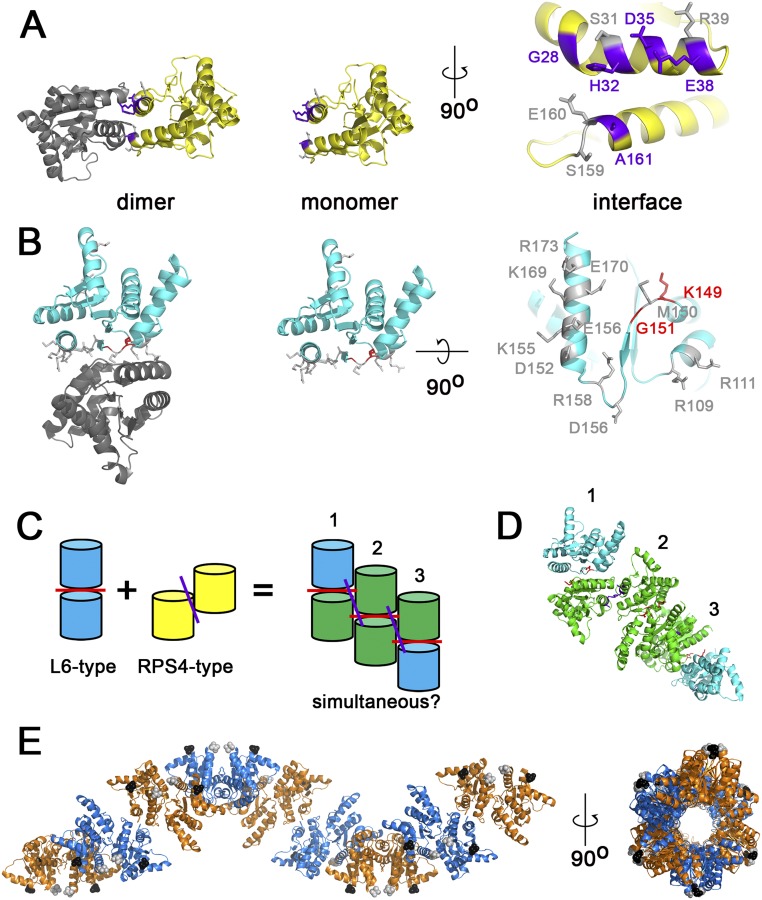
Fig. S3.
PyMOL modeling of RBA1 dimer mutants; hypothetical higher-order TIR complexes are sterically feasible (data related to Fig. 3). (A) L6-type RBA1 mutations. The RBA1 residues shown in purple lose autoactivity function when mutated. The residues shown in gray were dispensable for autoactivity. (B) RPS4-type RBA1 mutations. The RBA1 residues shown in red lose autoactivity function when mutated. The residues shown in gray were dispensable for autoactivity. (C) The TIR dimers for L6 and RPS4 interact on distinct surfaces. (D and E) Hypothetical models of RBA1 interacting simultaneously using both L6 and RPS4 interfaces. D shows a three-dimer chain color-coded as in C. In E, nine dimers form a helical structure around a central channel. Monomers from L6-type dimers share colors (either orange or marine); L6-type dimers are connected across colors by RPS4-type interfaces. The N and C termini of each monomer are indicated by black and gray spheres, respectively.